Leg Cramps During Pregnancy: First Aid Comfort Tips and Workplace Awareness in Canada
 Understanding Pregnancy-Related Leg Cramps
Understanding Pregnancy-Related Leg Cramps
Leg cramps are a common and often uncomfortable symptom during pregnancy. Many women notice sudden tightening or spasms in the calf muscles, especially at night. These cramps can be strong enough to interrupt sleep and may feel worse when the toes point downward. While brief stretching or standing can provide temporary relief, longer-term comfort usually depends on understanding contributing factors such as circulation changes, muscle strain, and nutrition.
First Aid & Workplace Relevance in Canada
Pregnant employees are active in many Canadian workplaces, and general first aid awareness helps coworkers respond with empathy and practical comfort measures. Simple actions — offering a chair, encouraging short stretch breaks, or supporting hydration — can reduce discomfort without drawing unwanted attention. Workplace wellness programs and first aid education often include guidance on muscle cramps and safe comfort strategies.
A Short Realistic Scenario
During a late afternoon shift, a pregnant employee feels a sudden calf cramp while sitting at a desk. A colleague familiar with basic first aid awareness suggests gently stretching the foot upward and taking a short walk. After a brief break and some water, the discomfort eases. The employee later adjusts seating posture and adds regular stretch breaks to help prevent repeat cramps.
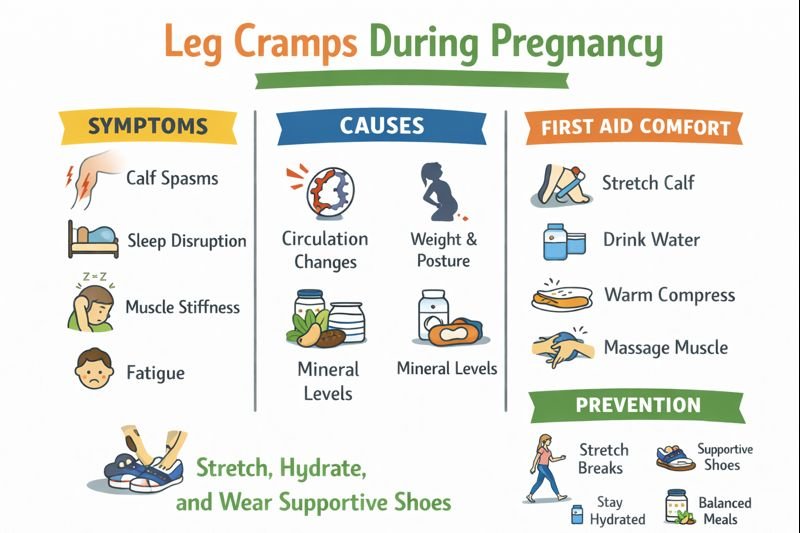
Common Symptoms
Pregnancy-related leg cramps may include:
-
Sudden tightening or spasms in the calf
-
Pain that wakes someone from sleep
-
Muscle stiffness after sitting or standing for long periods
-
Temporary soreness following a cramp
Cramps most often occur in the second and third trimesters but can vary by individual.
Causes and Contributing Factors
Circulation Changes
As pregnancy progresses, the growing uterus can place pressure on veins that return blood from the legs to the heart. This may lead to fluid buildup and muscle fatigue, increasing the likelihood of cramps. Resting with legs slightly elevated and gentle movement throughout the day can support circulation.
Weight and Posture
Natural weight gain and posture adjustments can strain muscles and nerves in the legs and lower back. Supportive footwear, regular light activity, and attention to sitting posture can help reduce tension.
Mineral and Nutrition Considerations
Calcium, magnesium, potassium, and vitamin D all play roles in muscle function. Some women may notice more frequent cramps if dietary intake is low or absorption is reduced. Balanced meals, adequate hydration, and routine prenatal nutrition discussions with a qualified professional can support overall comfort.
First Aid Comfort Measures (General Awareness)
For mild leg cramps:
-
Gently stretch the calf by flexing the foot upward.
-
Stand and walk slowly if comfortable.
-
Massage the affected muscle.
-
Apply a warm (not hot) compress to the area.
-
Drink water to support hydration.
These are comfort-focused measures intended for everyday awareness rather than treatment decisions.
Prevention and Workplace Considerations
-
Encourage regular stretch or movement breaks.
-
Use supportive footwear and ergonomic seating.
-
Elevate legs slightly during rest when possible.
-
Maintain steady hydration throughout the day.
-
Promote balanced meals and reasonable break schedules.
-
Support flexible lighting and quiet rest areas if fatigue is present.
-
Include pregnancy comfort topics in general workplace first aid or wellness training.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do leg cramps often happen at night?
Muscle fatigue and reduced movement during sleep can contribute to sudden tightening, especially later in pregnancy.
Does gentle exercise help?
Light activities such as walking or prenatal stretching may support circulation and muscle comfort for many individuals.
Can posture make a difference?
Yes. Supportive seating, proper footwear, and avoiding long periods in one position can reduce muscle strain.
Do minerals affect muscle cramps?
Balanced nutrition that includes calcium, magnesium, potassium, and vitamin D supports normal muscle function.
What can coworkers do in a workplace setting?
Offer a seat, encourage short stretch breaks, and support hydration in a respectful and low-key way.
Educational Note
This information is for general public education and first aid awareness. Pregnancy experiences vary, and learning simple comfort strategies can help individuals respond calmly to everyday muscle discomfort.