Diabetic Foot and Charcot Arthropathy: Awareness, Symptoms, and First Aid Education in Canada
What Is Diabetic Foot?
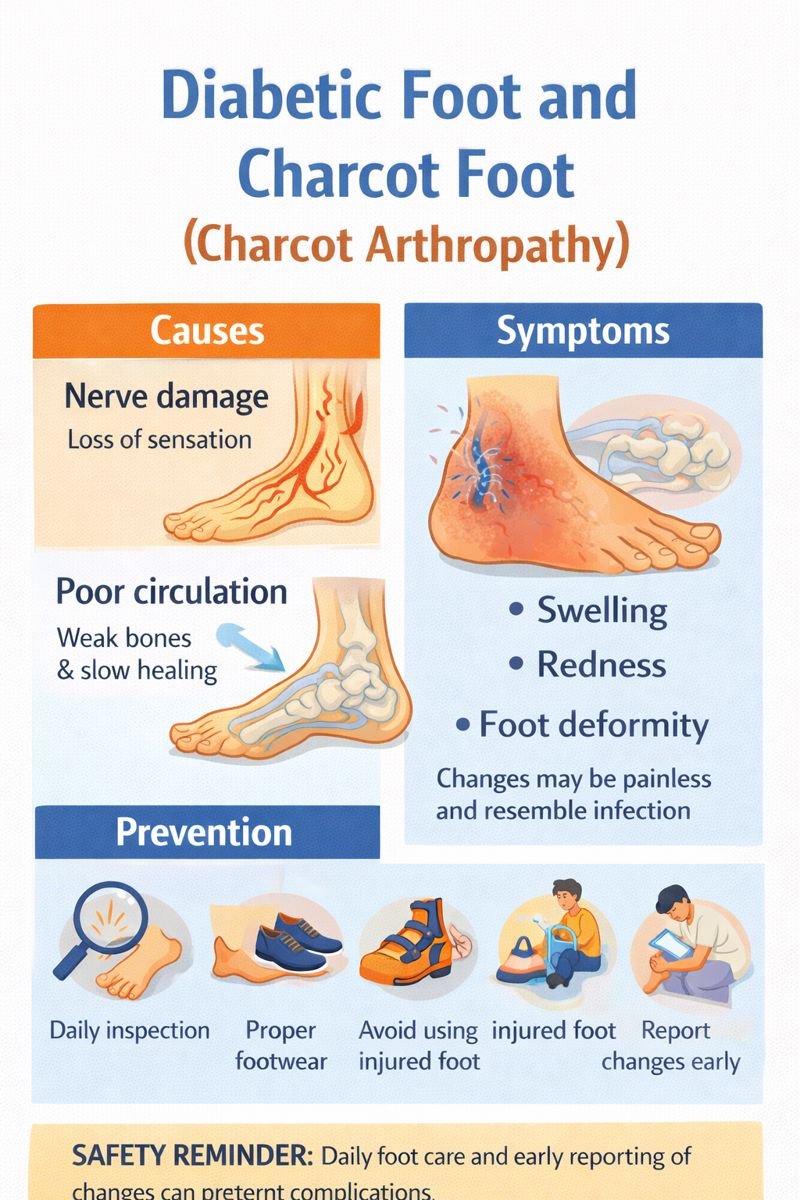
Diabetic foot refers to a range of foot problems that can develop in people living with diabetes. Diabetes affects millions of individuals worldwide and is a leading cause of foot-related hospitalizations. Many of these complications are linked to nerve damage and poor circulation, which can reduce sensation, slow healing, and weaken bones.
One of the most serious diabetic foot conditions is Charcot arthropathy (Charcot foot)—a disorder that can change the shape of the foot, damage joints, and lead to long-term disability if not recognized early.
First Aid and Workplace Relevance in Canada
Diabetic foot conditions are relevant in Canadian workplaces, especially for individuals who spend long hours standing, walking, or wearing protective footwear. Reduced sensation means injuries may go unnoticed, increasing the risk of infection and structural damage.
First aid awareness supports early recognition of foot changes, encourages prompt reporting of concerns, and reinforces the importance of daily foot checks as part of overall health and workplace safety.
A Simple, Realistic Scenario
A worker with diabetes notices swelling and warmth in one foot after a regular shift, even though they don’t recall any injury. Remembering first aid education, they avoid putting extra weight on the foot and arrange a medical assessment. Early evaluation helps prevent further damage.
Overview of Diabetic Foot Problems
Diabetes can affect the feet in two major ways:
-
Nerve damage (neuropathy): Reduced or lost sensation means cuts, pressure points, or minor injuries may go unnoticed.
-
Poor circulation: Reduced blood flow weakens bones and slows healing, increasing the risk of fractures and joint damage.
Together, these complications increase the likelihood of infections, ulcers, and bone or joint breakdown—sometimes without pain.
What Is Charcot Arthropathy?
Charcot arthropathy is a condition in which the bones and joints of the foot weaken and break down due to nerve damage and impaired circulation. Because sensation is reduced, individuals may continue walking on an injured foot, worsening the damage.
Over time, this can lead to:
-
Foot deformity
-
Joint instability
-
Difficulty walking or standing
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Charcot foot may not cause pain, especially in the early stages. Key signs include:
-
Swelling of the foot, often the earliest and most sensitive indicator
-
Redness or warmth in the foot
-
Changes in foot shape over time
Swelling and redness may appear without a clear injury. These changes can sometimes resemble infection on imaging, but infection is less likely when the skin is intact and no ulcer is present.
Diagnosing Diabetic Foot Conditions
Diagnosis begins with a review of overall health, symptoms, and any known foot injuries. A physical examination checks circulation, sensation, and structural changes.
Imaging may include:
-
X-rays, which may appear normal in early stages
-
Advanced imaging later, showing fractures or joint dislocations
-
Additional scans if bone infection is suspected
Early diagnosis is important to limit long-term damage.
Treatment and Management Considerations
-
Allow damaged bones to heal
-
Prevent further deformity
-
Protect joints and surrounding tissue
In early stages, treatment often involves immobilization of the foot using a cast or protective boot. This helps reduce swelling and protects the bones while healing begins.
Key aspects of early management may include:
-
Avoiding weight-bearing on the affected foot
-
Using mobility aids such as crutches or a wheelchair
-
Regular cast adjustments as swelling decreases
Healing may take several months, and close monitoring is often required.
Prevention and Foot Care Awareness
Prevention is the most effective approach to diabetic foot complications.
Important preventive measures include:
-
Daily inspection of the feet for swelling, redness, or skin changes
-
Wearing properly fitting footwear
-
Reporting foot changes early
-
Avoiding walking on an injured or swollen foot
-
Maintaining regular foot care routines
Education and awareness play a vital role in preventing serious complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are foot problems more serious for people with diabetes?
Nerve damage and poor circulation can hide injuries and slow healing.
Can Charcot foot occur without pain?
Yes. Many people experience swelling and redness without pain due to reduced sensation.
Is swelling an early sign of Charcot foot?
Yes. Swelling is often the earliest and most noticeable symptom.
Can diabetic foot problems be prevented?
Many complications can be reduced through daily foot checks and early care.
How does first aid training help with diabetic foot awareness?
First aid education promotes early recognition of warning signs and timely medical follow-up.
Educational Note
This article is intended for general public education and workplace first aid awareness in Canada. It does not replace medical assessment, diagnosis, or individualized treatment for diabetic foot conditions.
