Abscessed Tooth Pain: First Aid Awareness and Dental Safety in Canada
 Understanding an Abscessed Tooth
Understanding an Abscessed Tooth
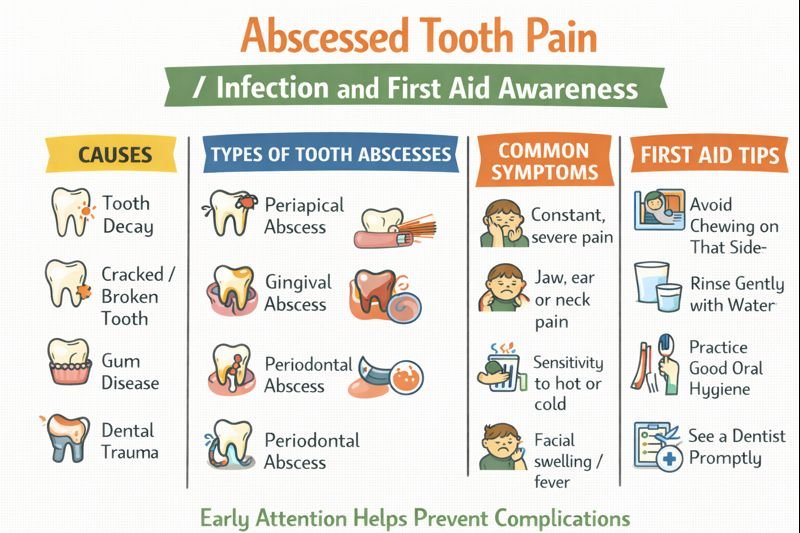
Pain from an abscessed tooth is very different from a mild or occasional toothache. While a simple toothache may come and go, an abscessed tooth usually causes constant, severe, and worsening pain. A tooth abscess forms when an infection develops inside the tooth or surrounding gum tissue, often due to untreated tooth decay, gum disease, or injury to the tooth. Because the infection can spread beyond the mouth, early recognition and prompt dental assessment are important.
First Aid & Workplace Relevance in Canada
Dental pain can significantly affect concentration, communication, and safety at work. In Canadian workplaces, first aid awareness helps coworkers recognize when pain may be more than routine discomfort and encourage rest, hydration, and timely professional care. Calm support can reduce stress and help prevent complications while the individual arranges dental treatment.
A Short Realistic Scenario
During a workday, an employee experiences a constant throbbing pain in their jaw that worsens when chewing. A colleague familiar with first aid awareness suggests avoiding food on the affected side, rinsing the mouth gently with water, and taking a break from talking tasks. The employee later contacts a dental clinic for assessment, preventing the pain from escalating further.
What Is a Tooth Abscess?
A tooth abscess is a pocket of infection that contains pus. It develops when bacteria enter the tooth or gums, commonly through:
-
Untreated tooth decay
-
Cracked or broken teeth
-
Gum disease
-
Dental trauma
The buildup of infection increases pressure in the area, leading to severe pain and swelling.
Types of Tooth Abscesses
Different abscesses can cause similar pain but involve different structures:
Periapical Abscess
-
Begins in the pulp at the centre of the tooth
-
Often linked to deep tooth decay or trauma
Gingival Abscess
-
Affects the gum tissue only
-
May be associated with food particles or plaque trapped under the gum
Periodontal Abscess
-
Develops in the bone and tissues supporting the teeth
-
Often linked to advanced gum disease
Common Symptoms
Abscessed tooth pain is often described as:
-
Constant, throbbing, or sharp pain
-
Pain spreading to the jaw, ear, neck, or face
Other symptoms may include:
-
Sensitivity to hot or cold
-
Pain when chewing or biting
-
Bad taste or unpleasant breath
-
Difficulty opening the mouth
-
Swelling in the gums, jaw, or face
-
Fever or general feeling of illness in more advanced cases
Symptoms can worsen quickly over hours or days.
First Aid Awareness and General Comfort Measures
While waiting for dental care:
-
Avoid chewing on the affected side.
-
Rinse the mouth gently with clean water.
-
Maintain good oral hygiene without aggressive brushing.
-
Sit upright to reduce pressure and discomfort.
-
Avoid applying heat to the face, which may worsen swelling.
These steps focus on comfort and awareness only and do not treat the infection.
Why Prompt Care Matters
An untreated tooth abscess can lead to serious complications, including:
-
Spread of infection to the jaw, face, or neck
-
Tooth loss
-
Widespread infection affecting other parts of the body
Early assessment helps reduce the risk of complications and supports better recovery outcomes.
Prevention and Workplace Considerations
-
Encourage regular dental checkups.
-
Promote oral hygiene awareness as part of overall wellness.
-
Support flexible scheduling for dental appointments when pain is severe.
-
Encourage early attention to tooth pain rather than waiting.
-
Include dental emergencies in basic first aid awareness discussions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is an abscessed tooth an emergency?
It can become serious if ignored. Persistent or severe dental pain should be assessed promptly.
Can an abscess go away on its own?
The pain may fluctuate, but the infection usually does not resolve without dental care.
Why does the pain spread to the jaw or ear?
Shared nerve pathways can cause pain to radiate beyond the tooth.
Is swelling always present?
Not always at first, but swelling may develop as the infection progresses.
How can coworkers help?
Encouraging rest, avoiding chewing, and supporting timely dental care can make a meaningful difference.
Educational Note
This information is provided for general public education and first aid awareness. Dental infections can progress quickly, and learning to recognize concerning symptoms supports calm and timely decision-making.