Tibial Growth Plate Fracture (Ankle): Symptoms, Causes, and First Aid Awareness in Canada
What Is a Tibial Growth Plate Fracture?
A tibial growth plate fracture occurs when there is a break at the growth plate near the ankle end of the tibia (shin bone). Growth plates are areas of developing cartilage found in children and adolescents. Because these areas have not yet fully hardened into bone, they are more vulnerable to injury than the surrounding bone.
These fractures typically occur before skeletal maturity, making them a condition seen almost exclusively in children and teenagers.
First Aid and Workplace / Community Relevance in Canada
While tibial growth plate fractures do not occur in adults, they are relevant in Canadian community, school, and recreational settings. Falls during play, sports, cycling, skating, or organized athletics are common causes.
First aid awareness is important for parents, coaches, educators, and caregivers, as early recognition and appropriate response can help protect normal bone growth and recovery.
A Simple, Realistic Scenario
A teenager falls while running during a school sports activity and twists their ankle. They are unable to put weight on the foot, and swelling develops quickly. A supervising adult, familiar with first aid principles, keeps the ankle still, avoids further movement, and arranges prompt medical assessment.
Common Symptoms
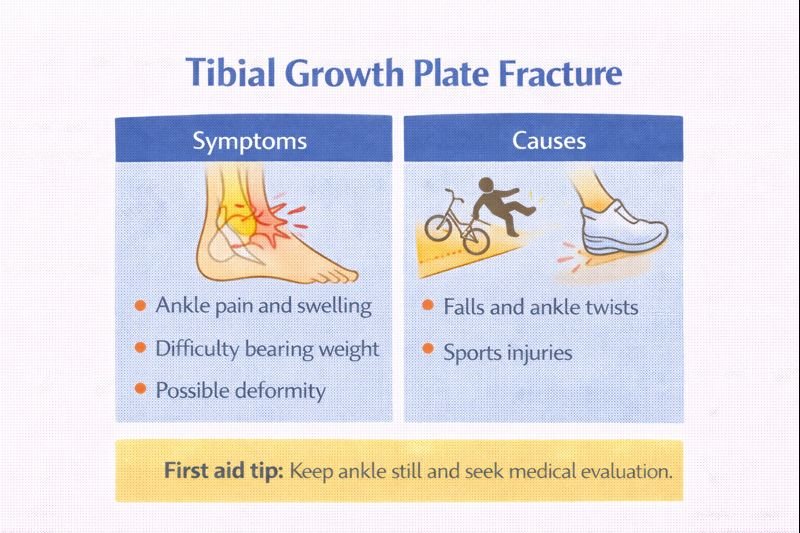
-
Difficulty or inability to bear weight
-
Rapid swelling around the ankle
-
Pain with ankle movement
-
Visible deformity in more severe or displaced fractures
In overuse-related cases, pain may:
-
Develop gradually
-
Appear during activity
-
Improve with rest
Understanding Growth Plate Injuries
Long bones, such as the tibia, grow from specialized areas at their ends called growth plates. These plates are made of cartilage and are the last parts of the bone to harden as a child grows.
Because growth plates are softer than mature bone:
-
They fracture more easily
-
Injuries may not always be obvious on standard X-rays
-
Proper assessment is especially important
Ankle injuries in children are more likely to involve the growth plate than the ligaments seen in adult ankle sprains.
Causes of Tibial Growth Plate Fractures
Growth plate fractures may occur due to:
-
Falls while running or playing
-
Twisting injuries to the ankle
-
Falls from bicycles, playground equipment, or sports activities
Less commonly, they may develop as overuse injuries, particularly in:
-
Long-distance running
-
Gymnastics
-
Sports involving repetitive impact
In these cases, pain tends to build gradually rather than occurring suddenly.
First Aid Awareness and Early Response
From a first aid perspective, suspected growth plate fractures should be managed cautiously.
General first aid considerations include:
-
Stopping activity immediately
-
Keeping the ankle still and supported
-
Avoiding weight-bearing
-
Arranging prompt medical evaluation
Early care helps reduce the risk of further injury to the growth plate.
Medical Assessment and Treatment Considerations
Medical evaluation is essential when a growth plate fracture is suspected.
Assessment may involve:
-
Imaging to confirm the injury
-
Additional scans if the growth plate is not clearly visible
Treatment depends on:
-
Severity of the fracture
-
Whether the bone is displaced
Management may include:
-
Immobilization with a cast for several weeks in minor fractures
-
Realignment of the bone if displacement is present
-
Immobilization following realignment to allow healing
After immobilization, gradual rehabilitation is used to restore:
-
Movement
-
Strength
-
Balance
Importance of Follow-Up
Because growth plates are involved in bone development, follow-up care is important to ensure proper healing and normal growth of the bone.
Early recognition and appropriate management reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are growth plate fractures unique to children?
Growth plates close once bone growth is complete, so adults do not have them.
Can growth plate fractures be missed on X-rays?
Yes. Growth plates are cartilage and may not be clearly visible early on.
Is weight-bearing safe after this injury?
Weight-bearing is usually limited until healing progresses.
Can overuse cause growth plate injuries?
Yes. Repetitive stress can irritate or injure growth plates over time.
How does first aid training help with childhood fractures?
First aid education supports early recognition, safe immobilization, and timely care.
Educational Note
This article is intended for general public education and first aid awareness in Canada. It does not replace medical assessment, diagnosis, or individualized treatment for bone injuries in children or adolescents.
