Understanding Celiac Disease & Gluten Sensitivity
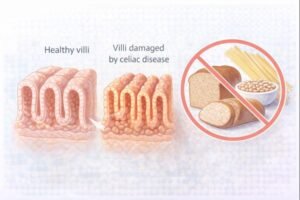
The condition is relatively common in Canada and can affect both children and adults. People may experience digestive symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, bloating, constipation, or poor weight gain. Some also present with less obvious symptoms including fatigue, anemia, or delayed growth in children.
What Causes Celiac Disease?
Celiac disease is an autoimmune condition, not a food intolerance or allergy. When gluten is eaten, the immune system attacks the lining of the small intestine. Over time, this causes villous atrophy (flattening of the intestinal lining) and reduces nutrient absorption.
Researchers believe causes are linked to:
-
Genetics (family history increases risk)
-
Environmental triggers
-
Immune system factors
Celiac disease appears more often in women than men and can develop at any age. A higher number of diagnoses occur in early childhood or mid-to-late adulthood.
Foods That Contain Gluten
Gluten occurs naturally in:
-
Wheat
-
Barley
-
Rye
Common gluten-containing foods include:
-
Bread & baked goods
-
Pasta & noodles
-
Breakfast cereals
-
Cakes, pastries & crackers
-
Soups, sauces & convenience meals (depending on ingredients)
-
Some beers brewed from barley
Food safety plays a key role. In Canada, packaged foods must clearly indicate whether gluten-containing ingredients are present — an important protection for those with medical dietary restrictions.
Symptoms to Watch For
Symptoms can vary widely. Some individuals develop traditional digestive symptoms, while others show non-digestive signs.
Digestive symptoms may include:
-
Abdominal pain
-
Bloating or gas
-
Diarrhea or constipation
-
Weight loss
-
Nausea
Other possible symptoms include:
-
Fatigue or low energy
-
Iron deficiency anemia
-
Poor growth in children
Even mild or intermittent symptoms warrant attention since untreated celiac disease can lead to long-term nutritional deficiencies.
Diagnosis & Screening
There is currently no single universal screening program in Canada, but testing is recommended for people with symptoms or first-degree relatives of individuals with celiac disease.
Diagnosis often involves:
-
Blood testing for antibodies
-
Medical assessment
-
Endoscopy with biopsy (in some cases)
Treatment & Living Well With Celiac Disease
There is no cure, but a strict gluten-free diet allows the intestine to heal and prevents future complications. A gluten-free diet has become easier to maintain in Canada due to expanded retail options, clearer food labelling, and increased awareness.
Managing celiac disease may also involve:
-
Working with a dietitian
-
Monitoring nutrient levels
-
Learning to read food labels carefully
Untreated celiac disease can lead to:
-
Vitamin deficiencies
-
Osteoporosis
-
Iron deficiency anemia
-
Pregnancy-related complications (less common)
-
Rarely, certain bowel cancers long-term
Workplace & Training Relevance in Canada
Celiac disease has implications for food handling and safe meal preparation. In workplaces involving food service, childcare, education, camps, or long-term care, staff should understand dietary restrictions to avoid accidental gluten exposure.
St. Mark James Training offers courses that help Canadians build knowledge around:
-
Food safety certification — relevant for preventing cross-contact with allergens and gluten
-
First aid and CPR training — beneficial for all workplaces and community settings
-
Workplace safety training — supports inclusive and safer environments for staff and the public
Educational Note (Non-Clinical Disclaimer)
This post is intended for general learning only. It does not provide medical diagnosis or treatment. Anyone experiencing symptoms or nutrition concerns should speak with a qualified healthcare professional in Canada.
