Insect Sting Allergies in Canada: Reactions, Symptoms & First Aid Awareness
-
Bees
-
Wasps
-
Hornets
-
Yellow jackets
-
Fire ants (less common in most regions but included in allergy literature)
Most insect stings do not cause allergic reactions. Many people mistake a normal local reaction (pain, swelling, redness) for an allergy. Knowing the difference helps guide when to seek care and when home first aid is appropriate.
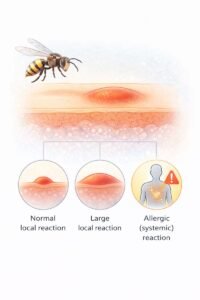
Types of Reactions
Not all sting reactions are the same. They can be grouped into three broad categories:
1. Normal local reaction
-
Pain, redness, and mild swelling around the sting site
-
Discomfort usually subsides within hours to a couple of days
2. Large local reaction
-
Swelling spreads beyond the sting area (e.g., entire forearm after a sting to the hand)
-
May look concerning but typically resolves without progressing to a systemic reaction
3. Allergic (systemic) reaction
-
Involves multiple body systems
-
Can range from mild to severe, and may develop rapidly
Severe systemic reactions may indicate anaphylaxis, which is a medical emergency and requires immediate care.
Symptoms of a Severe Allergic Reaction (Anaphylaxis)
A severe allergic reaction may include one or more of the following:
-
Hives or widespread itching
-
Swelling of lips, face, mouth, or throat
-
Difficulty breathing or wheezing
-
Rapid heartbeat
-
Trouble swallowing
-
Lightheadedness, dizziness, or fainting
-
Anxiety or restlessness
Anaphylaxis can progress quickly. Immediate medical assessment is important, and severe cases may require emergency interventions.
Mild Local Sting Reactions
Mild reactions at the sting site may include:
-
Local redness or itching
-
Mild to moderate swelling
-
Tenderness or warmth
-
Small pimple-like bumps
These reactions are uncomfortable but not life-threatening and can often be cared for at home.
First Aid for Local Reactions
Supportive care may include:
-
Removing rings or jewelry if the sting is on the hand
-
Checking for a stinger (scrape gently; do not pinch)
-
Washing with soap and water
-
Using topical hydrocortisone or antihistamines for itching
-
Applying cold packs for swelling or discomfort
First Aid for Allergic Reactions
Severe allergic reactions may require:
-
Epinephrine auto-injector, if prescribed
-
Calling emergency medical services (9-1-1 in Canada)
-
Monitoring breathing and responsiveness
-
Additional medical treatments such as oxygen or IV fluids at the hospital
Prompt action can prevent symptoms from worsening.
Why First Aid Training Matters in Canada
Anaphylaxis is a time-sensitive emergency. First aid and CPR/AED training through St. Mark James Training equips Canadians to recognize allergic reactions early, administer epinephrine if appropriate, and activate emergency services. Many workplaces, camps, sports organizations, and childcare environments include allergy training in their safety programs.
Educational Disclaimer
This article provides general public education in a Canadian context and does not replace medical assessment or emergency care. If a severe allergic reaction is suspected, call 9-1-1 in Canada.
