Scaphoid Wrist Fracture: Symptoms, Causes, and First Aid Awareness in Canada
What Is a Scaphoid Wrist Fracture?
The scaphoid is one of the smallest bones in the wrist, located on the thumb side, where the wrist bends. It sits at the base of the hollow formed when the thumb is extended—often noticed when making a “hitchhiking” position. Because of its size and position, the scaphoid is prone to injury, especially during falls.
Pain or tenderness in this hollow area can be an early sign of a scaphoid injury. These fractures are sometimes difficult to recognize right away and may initially be mistaken for a wrist sprain.
First Aid and Workplace Relevance in Canada
Scaphoid fractures are relevant in many Canadian workplaces and recreational settings, including construction, transportation, sports, and winter activities where slips and falls are common. A simple fall onto an outstretched hand can lead to this injury.
First aid awareness helps individuals recognize fracture injury warning signs early, protect the wrist, and seek timely medical assessment—reducing the risk of long-term complications or delayed healing.
A Simple, Realistic Scenario
A recreational hockey player slips on ice and lands on an outstretched hand. Their wrist feels sore but doesn’t look deformed. Remembering first aid training, they limit wrist movement and seek medical evaluation the next day when pain near the base of the thumb hasn’t improved.
Common Causes of Scaphoid Fractures
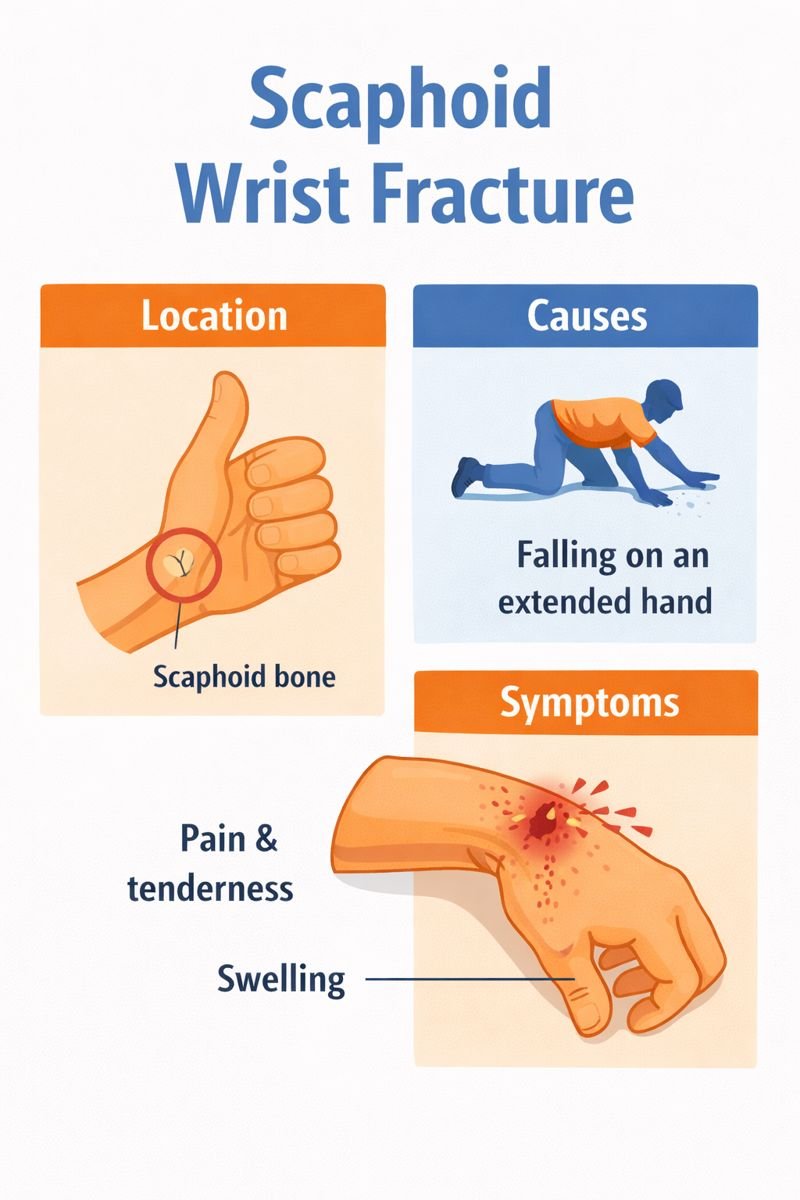
Common situations include:
-
Slips and falls
-
Sports-related impacts
-
Motor vehicle or cycling incidents
Scaphoid fractures can occur at any age, including in children, but are more frequently seen in young adults, particularly during high-impact activities. There are no specific medical conditions that increase the risk, though studies suggest that wrist guards during certain sports may help reduce wrist injuries.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
Symptoms of a scaphoid fracture may include:
-
Pain or tenderness at the base of the thumb
-
Swelling around the wrist
-
Increased pain when moving the wrist or thumb
-
Difficulty gripping or holding objects
In some cases, pain may be mild at first and mistaken for a simple sprain. The wrist may appear normal without obvious deformity. Wrist pain that lasts more than a day after an injury should be medically assessed to rule out a fracture.
First Aid and General Management
From a first aid perspective, early care focuses on protecting the wrist and reducing movement after an injury.
General first aid considerations include:
-
Supporting or immobilizing the wrist
-
Avoiding activities that increase pain
-
Monitoring swelling and discomfort
-
Seeking medical evaluation if pain persists
Prompt assessment is important because scaphoid fractures can be difficult to see on early imaging and may heal slowly if not properly managed.
Medical Management and Healing Considerations
Treatment depends on where the fracture occurs within the scaphoid bone.
-
Fractures closer to the thumb tend to heal more quickly due to better blood supply and may require a cast below the elbow, sometimes including the thumb.
-
Fractures closer to the forearm heal more slowly because of reduced blood flow and may require longer immobilization or a cast that extends above the elbow.
Healing times vary between individuals, and medical professionals typically monitor recovery using imaging over time.
Prevention and Workplace Safety Tips
Reducing the risk of wrist injuries involves awareness and protective strategies.
Helpful prevention measures include:
-
Wearing wrist guards during higher-risk sports
-
Using proper footwear to reduce slip hazards
-
Maintaining clear walkways in workplaces
-
Practising safe movement techniques during physical tasks
Early reporting of wrist injuries in the workplace can help prevent complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are scaphoid fractures sometimes missed at first?
Pain may be mild initially, and the wrist may not look deformed, making the injury easy to mistake for a sprain.
Where is scaphoid pain usually felt?
Pain is commonly felt at the base of the thumb in the hollow area of the wrist.
Can a scaphoid fracture heal on its own?
Healing depends on proper immobilization and location of the fracture, which is why medical assessment is important.
Are scaphoid fractures common in sports?
Yes. Falls onto an outstretched hand during sports are a frequent cause.
How does first aid training help with wrist injuries?
First aid training helps with early recognition, immobilization, and knowing when medical evaluation is needed.
Educational Note
This article is intended for general education and workplace first aid awareness in Canada. It does not replace medical assessment, diagnosis, or treatment of wrist injuries.
