Abdominal Bloating: Causes, Relief, and When to Seek Medical Care
Abdominal bloating is a common condition described as a sensation of fullness, tightness, or pressure in the abdomen. While bloating may feel uncomfortable, it is often not caused by a serious medical issue.
It is important to understand that bloating is different from abdominal swelling. With bloating, the abdomen may feel tight or distended without visibly increasing in size, although both can sometimes occur together.
In many cases, bloating is linked to excessive gas, digestive sensitivity, or dietary factors. However, if bloating is persistent, severe, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms, medical assessment is recommended.
Common Causes of Abdominal Bloating
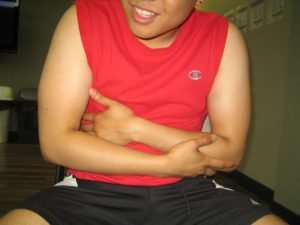
Abdominal bloating most often occurs due to issues affecting digestion or gas movement through the intestines. Common causes include:
- Excessive gas related to irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Difficulty digesting certain foods (such as lactose or high-fiber foods)
- Eating too quickly or swallowing excess air
- Carbonated beverages
- Constipation
- Sensitivity to specific carbohydrates (FODMAPs)
While bloating is usually harmless, new, worsening, or unexplained bloating should always be discussed with a healthcare provider.
How Is Abdominal Bloating Managed?
Treatment for abdominal bloating depends on the underlying cause. In many cases, symptoms improve with dietary and lifestyle changes, including:
Practical Self-Care Strategies
-
Avoid carbonated beverages
-
Limit foods known to increase gas, such as:
-
Cabbage
-
Brussels sprouts
-
Lentils
-
Beans
-
-
Avoid chewing gum, which increases swallowed air
-
Eat slowly and consume small, frequent meals
-
Be cautious with fiber intake—some forms (such as psyllium) may worsen bloating in individuals with IBS
-
Drink fennel tea, which may help reduce gas and discomfort
Medications
Some individuals find partial relief using over-the-counter products such as:
- Simethicone
- Activated charcoal
These treatments may reduce gas but do not work for everyone and do not address the root cause of bloating.
When to Seek Medical Care
You should consult a doctor if abdominal bloating is:
- Persistent or progressively worsening
- Severe or painful
- Associated with unexplained weight loss
- Accompanied by vomiting, blood in stool, fever, or changes in bowel habits
Early assessment helps rule out more serious digestive or systemic conditions.
First Aid & Health Awareness Note (Canada)
Understanding common digestive symptoms like abdominal bloating is part of broader first aid and health awareness. Knowing when symptoms are manageable at home—and when to seek medical care—is an important skill taught in Canadian first aid education.
👉 Learn more about recognizing medical symptoms and emergencies by taking a Standard First Aid & CPR course through St Mark James Training, Canada’s largest 100% Canadian-owned and operated first aid and CPR training provider.
