Heart Failure: Understanding the Condition and How It Affects the Body
Heart failure is a serious, long-term medical condition in which the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently enough to meet the body’s needs. While there is currently no cure, many people living with heart failure are able to lead active and meaningful lives through proper medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and strong support systems.
Early recognition and ongoing management are key to slowing progression and improving quality of life.
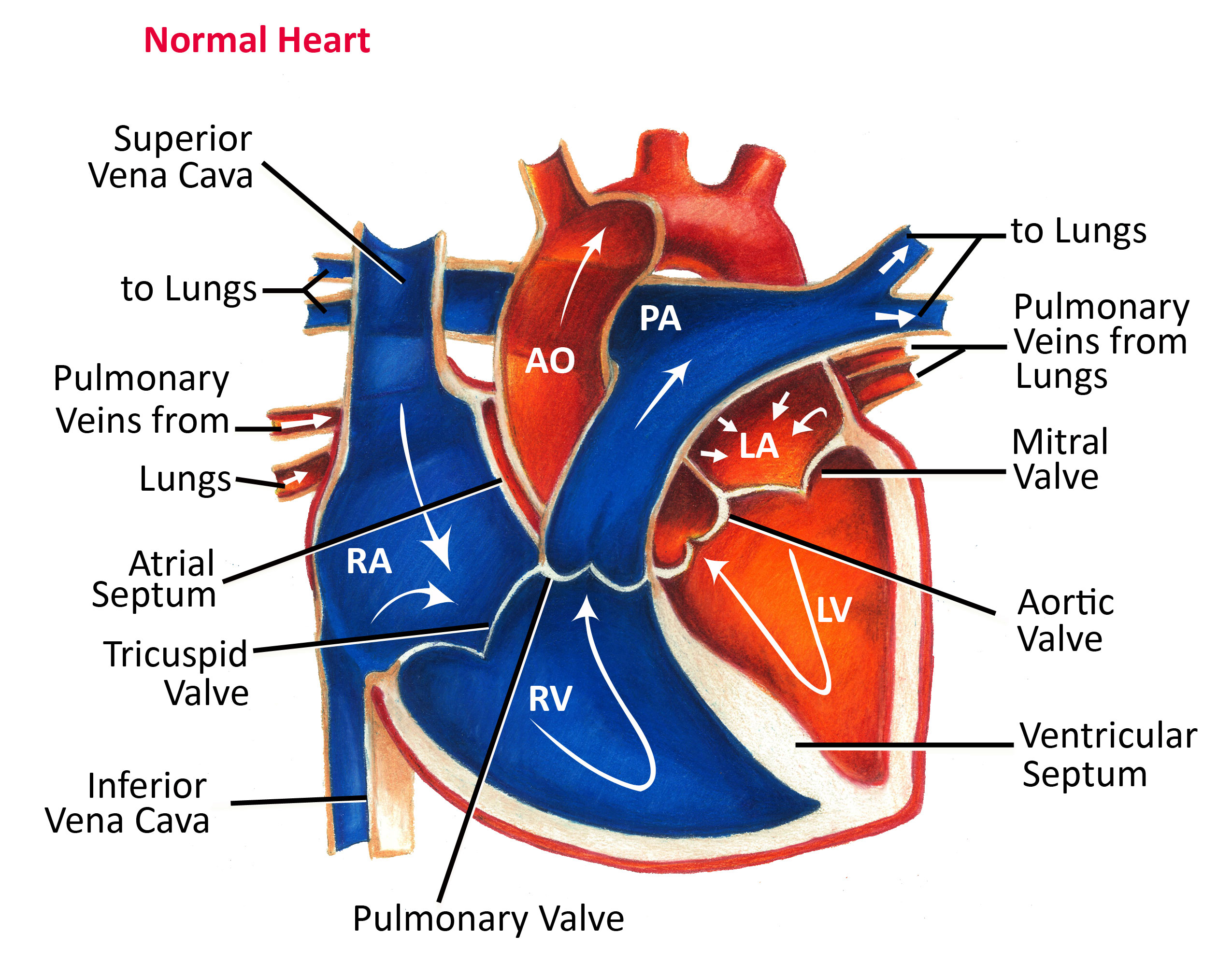
How a Normal Heart Works
A healthy heart is a strong, muscular pump that continuously circulates blood throughout the body. It is made up of four chambers:
-
Two upper chambers (atria)
-
Two lower chambers (ventricles)
The normal flow of blood occurs as follows:
-
Deoxygenated blood from the body enters the right atrium
-
Blood moves into the right ventricle and is pumped to the lungs
-
Oxygen-rich blood returns from the lungs to the left atrium
-
Blood enters the left ventricle, which pumps it throughout the body
These chambers contract in a coordinated and rhythmic sequence, allowing the heart to function efficiently.
What Happens in Heart Failure
Heart failure develops when the heart muscle becomes too weak or stiff to pump blood effectively. Over time, the heart struggles to meet the body’s demands for oxygen and nutrients.
How the Heart Tries to Compensate
In the early stages, the body attempts to compensate in several ways:
-
Enlargement of the heart
The chambers stretch to hold more blood, allowing stronger contractions. Over time, this leads to fluid retention, lung congestion, and irregular heart rhythms. -
Thickening of the heart muscle
The muscle cells enlarge to increase pumping strength, but this eventually reduces flexibility and efficiency. -
Faster heart rate
The heart beats more quickly to increase blood output, placing additional strain on the heart muscle.
The body also responds by narrowing blood vessels to maintain blood pressure and redirecting blood away from less vital organs.
These measures may temporarily mask symptoms but do not correct the underlying problem. As heart failure progresses, the heart and body can no longer keep up with these demands.
When Symptoms Appear
As compensation mechanisms fail, individuals may begin to experience symptoms such as:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue and weakness
- Fluid buildup in the lungs or limbs
- Reduced ability to exercise or perform daily activities
These symptoms often prompt individuals to seek medical care and may signal advancing heart failure.
Living With Heart Failure
Although heart failure is a chronic condition, effective management can significantly improve outcomes. Treatment plans often include:
-
Medications to reduce strain on the heart
-
Lifestyle changes such as healthy eating, physical activity, and fluid management
-
Monitoring symptoms and weight changes
-
Emotional and practical support from family and caregivers
First Aid & Medical Disclaimer
This content is provided for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Heart failure is a serious condition that requires ongoing medical supervision.
Understanding how heart failure affects the body is an important part of first aid awareness and emergency preparedness. To learn how to recognize circulatory emergencies, respond to cardiac symptoms, and provide life-saving care, consider enrolling in a First Aid and CPR course with a certified Canadian training provider.