Dehydration: Signs, Effects, and First Aid Awareness in Canada
What Is Dehydration?
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluid than it takes in. Water is essential for circulation, temperature control, digestion, and brain function. When fluid levels drop too low, the body cannot perform at its best.
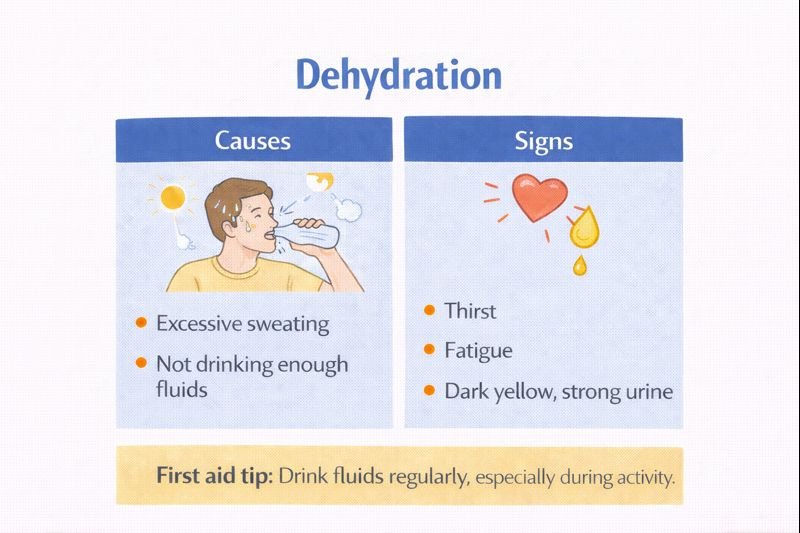
Dehydration can develop due to illness, fluid losses from the gastrointestinal tract, inadequate fluid intake, or excessive sweating, particularly during physical activity or hot conditions.
First Aid and Workplace Relevance in Canada
Dehydration is a common concern in Canadian workplaces and recreational settings, especially in construction, outdoor work, manufacturing, warehousing, fitness, and sports. Warm environments, protective clothing, and sustained physical effort all increase fluid loss.
First aid awareness helps individuals recognize early signs of dehydration, respond promptly, and prevent progression to more serious heat-related conditions.
A Simple, Realistic Scenario
During a summer shift, a landscaping worker begins to feel fatigued and unfocused. Their heart rate feels faster than usual, and they haven’t had much to drink. Remembering first aid training, they take a break in the shade, drink fluids, and monitor symptoms before returning to work.
How Dehydration Develops During Activity
When the body is active—especially during exercise or work in warm conditions—it loses fluid through:
-
Sweating, which helps regulate body temperature
-
Breathing, as moisture is released with increased respiration
If these losses are not replaced, dehydration can develop even over a short period of time.
How Dehydration Affects Performance
A fluid loss of around 2% of body weight has been associated with:
-
Increased heart rate
-
Slower reaction time
-
Reduced endurance and aerobic capacity
-
Impaired concentration and decision-making
-
Reduced alertness and judgment
As fluid levels drop, blood volume decreases and becomes thicker. This places additional strain on the heart as it works harder to supply oxygen to muscles and organs.
Heat and Circulation Effects
With continued dehydration:
-
Blood flow is prioritized to working muscles
-
Less blood reaches the skin
-
Sweating becomes less effective
This reduces the body’s ability to cool itself, allowing body temperature to rise. Without intervention, this can increase the risk of heat-related illness.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Dehydration
Dehydration may present with:
-
Thirst
-
Fatigue
-
Elevated heart rate
-
Reduced focus or coordination
-
Dark, strong-smelling urine
-
Decreased urine output
Monitoring early symptoms is important, as thirst often appears after dehydration has already begun.
First Aid and Early Management
From a first aid perspective, early response focuses on fluid replacement and rest.
General first aid measures may include:
-
Stopping or reducing activity
-
Moving to a cooler environment
-
Drinking fluids gradually
-
Monitoring for improvement in symptoms
Prompt action can help restore hydration before more serious effects develop.
Preventing Dehydration
Prevention is the most effective strategy.
Helpful hydration practices include:
-
Drinking fluids regularly throughout the day
-
Increasing fluid intake during physical activity or heat
-
Taking scheduled drink breaks rather than waiting for thirst
During exercise or prolonged activity, fluids should be consumed before, during, and after activity.
General Hydration Timing Guide
A commonly used general guide for fluid intake around exercise includes:
-
10–15 oz (300–450 mL) 2–3 hours before activity
-
8–10 oz (240–300 mL) about 15 minutes before activity
-
8–10 oz (240–300 mL) every 15 minutes during activity
Individual needs vary depending on conditions, activity level, and environment.
Monitoring Hydration Status
Urine colour can provide a simple hydration check:
-
Light or pale yellow urine usually indicates adequate hydration
-
Dark, concentrated urine with strong odour suggests dehydration
This method can help identify early fluid deficits.
Workplace and Activity Considerations
To reduce dehydration risk:
-
Schedule regular hydration breaks
-
Adjust workloads in hot conditions
-
Wear breathable clothing when possible
-
Encourage team awareness of early symptoms
Hydration planning is a key part of workplace health and safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can dehydration affect concentration?
Yes. Reduced fluid levels can impair focus, reaction time, and decision-making.
Is thirst a reliable sign of hydration status?
Not always. Thirst may be delayed during activity or masked by exertion.
Why does heart rate increase with dehydration?
Lower blood volume forces the heart to work harder to circulate oxygen.
Can dehydration develop in cooler weather?
Yes. Fluid loss still occurs through breathing and physical exertion.
How does first aid training help with dehydration?
First aid education improves early recognition and encourages timely fluid replacement.
Educational Note
This article is intended for general public education and workplace first aid awareness in Canada. It does not replace medical assessment, diagnosis, or individualized treatment for dehydration or heat-related conditions.
