Internal Bleeding Awareness: Signs, Risks & When to Seek Care
Relevance in First Aid & Canadian Workplaces
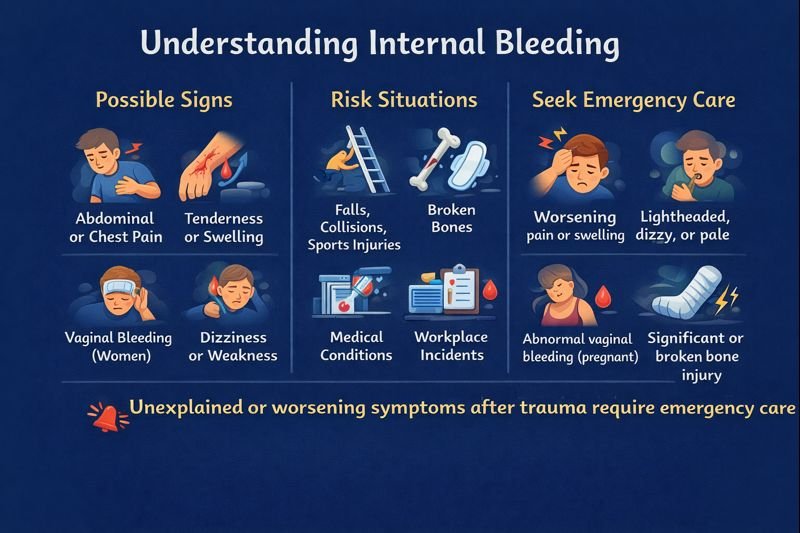
Falls, vehicle collisions, sports injuries, and workplace incidents can all involve internal injuries. First aid programs in Canada emphasize recognizing red flags and activating emergency response systems—not diagnosis or treatment. Prompt recognition of internal injuries and calling for help can influence outcomes when serious injuries are involved.
Scenario: Mild, Realistic & Non-Dramatic
A cyclist tipped over after braking suddenly during a weekend ride. Although they had only minor scrapes, they complained of worsening pain in their side over the next few hours and felt unusually tired. A friend encouraged them to visit the emergency department. Imaging later showed internal bruising that required observation but no surgery.
Causes & Risk Situations
Internal bleeding can result from:
-
Blunt injuries (sports, vehicle collisions, falls, workplace impacts)
-
Broken bones, especially large bones such as the femur or pelvis
-
Certain medical conditions affecting blood vessels or organs
-
Complications during pregnancy
-
Medications or bleeding disorders (healthcare evaluation required)
Possible Signs of Internal Bleeding (Awareness Only)
Symptoms vary greatly depending on location, severity, and the person’s health status. Awareness signs may include:
Abdominal or Chest Pain
Pain in the abdomen or chest can occur if organs or tissues are injured. Pain may stay in one spot or radiate to the back, jaw, or shoulder.
Tenderness or Swelling
The area may become firm, swollen, or sensitive to touch after trauma, although this varies widely.
Vaginal Bleeding
In women, abnormal vaginal bleeding can have many causes, including pregnancy-related complications. Healthcare assessment is essential.
Broken Bones
Large bone fractures can bleed internally into surrounding tissues. Rib fractures can cause internal injury to the lungs or other organs.
Dizziness, Weakness, or Fatigue
A drop in circulating blood volume may lead to light-headedness, pale skin, or general weakness.
Changes in Pulse or Breathing
These changes may occur as the body responds to blood loss. Only trained medical professionals should assess vital signs for diagnosis.
What Not to Do
Internal bleeding cannot be confirmed or managed safely without medical evaluation. It is not appropriate to:
-
Attempt to diagnose internal injuries
-
Palpate or press on painful areas
-
Use blood pressure cuffs or stethoscopes to “check” for bleeding
-
Delay medical care to perform assessments
These actions can be inaccurate and potentially harmful.
When to Seek Emergency Care
Emergency medical assessment is recommended when:
-
There is a significant blow to the body (e.g., fall, collision, sports hit) followed by worsening pain
-
Symptoms include dizziness, faintness, confusion, or unusual fatigue
-
Abdominal pain radiates to the back, jaw, or shoulder
-
There is abnormal vaginal bleeding, especially during pregnancy
-
Breathing becomes difficult
-
There is a suspected broken bone
Persistent or worsening symptoms should never be ignored after trauma.
Prevention & Workplace Considerations
Reducing the risk of internal injuries may involve:
-
Fall prevention (railings, flooring, ladder safety)
-
Protective gear for sports and trades
-
Safe driving and equipment operation
-
Clear reporting of workplace incidents
-
Encouraging early medical evaluation after moderate injuries
FAQ
1. Can internal bleeding occur without visible injury?
Yes. Some internal injuries do not produce external bruising or bleeding.
2. Is abdominal pain always a sign of internal bleeding?
No. Abdominal pain has many causes. Persistent or worsening pain after injury should be assessed.
3. Can internal bleeding be treated at home?
No. Internal bleeding requires medical evaluation and, in some cases, urgent treatment.
4. Why is internal bleeding dangerous?
Blood can accumulate in organs or tissues and affect organ function or blood pressure.
5. Should people wait for symptoms to “show up” after an injury?
Not necessarily. Some injuries require timely medical care even before symptoms become obvious.
Educational Note
This article supports public awareness of internal bleeding and when to seek medical care. It does not diagnose, treat, or provide emergency medical instructions. Healthcare professionals determine appropriate care.
