Constipation: Causes, Management & Prevention (Canada-Focused First Aid Education)
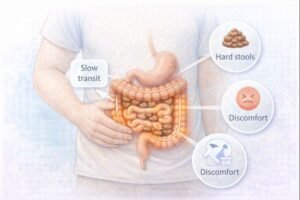
Constipation is a common digestive concern that affects Canadians of all ages. It occurs when a person passes stools less frequently than usual or has difficulty fully emptying their bowels. Stools may become hard, dry, small, or unusually large, making bowel movements uncomfortable.
Constipation can be temporary, but prolonged symptoms may impact daily functioning, diet, mood, physical activity, and overall quality of life.
Common Causes of Constipation
-
Low dietary fibre intake (e.g., limited fruits, vegetables, cereals, whole grains)
-
Not drinking enough fluids
-
Ignoring or delaying the urge to pass stool
-
Reduced physical activity
-
Changes in routine (travel, stress, lifestyle adjustments)
-
Certain medications (e.g., opioids, iron supplements, some antacids)
-
Stress, anxiety, or low mood
In children, constipation may also relate to:
-
Toilet training concerns
-
Fear of using unfamiliar bathrooms
-
Limited fluids or fibre intake
Constipation affects women more often than men, and is especially common during pregnancy and among older adults in Canada.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Constipation often improves with dietary and lifestyle adjustments. However, a healthcare professional should be consulted if:
-
Symptoms persist for several weeks
-
Pain during bowel movements becomes severe
-
There is blood in the stool
-
There is unexplained weight loss
-
Constipation occurs frequently in a child
Children should be assessed early, as prolonged bowel difficulties can lead to discomfort and feeding or behavioural challenges.
Management & Prevention
Most constipation improves through supportive care, including:
Diet & Lifestyle Measures
-
Increase fibre gradually (berries, apples, oats, lentils, cereals, vegetables)
-
Drink water regularly throughout the day
-
Engage in daily physical activity
-
Respond promptly to the urge to pass stool
-
Allow time and privacy in the bathroom
If lifestyle changes are not effective, a healthcare provider may recommend laxatives or other treatments. These may take several months to re-establish a regular pattern.
Possible Complications (Less Common)
Persistent constipation may contribute to:
-
Hemorrhoids
-
Bowel incontinence
-
Fecal impaction (stool buildup that becomes very difficult to pass)
Early management reduces the likelihood of these complications.
Canadian First Aid & Workplace Considerations
While constipation is primarily a health and lifestyle concern, awareness matters in both workplace safety and first aid education:
-
Employees experiencing discomfort or dehydration may be less focused at work
-
Certain job environments (e.g., heat exposure, limited bathroom access) may contribute to dehydration and bowel changes
-
Food safety and hygiene practices—taught in many Canadian safety programs—help prevent infectious diarrheal illnesses that can disrupt bowel health
St Mark James Training offers first aid, CPR/AED, and workplace safety courses across Canada that help Canadians build confidence in responding to common health issues, recognizing when medical attention may be needed, and supporting safe environments for children and adults.
Educational Disclaimer
This article is for general Canadian first aid education only and is not a diagnostic guide or medical treatment plan. If you have concerns about constipation or other digestive symptoms, consult a healthcare professional.
