Plugged Ears: Common Causes and When to Get Checked
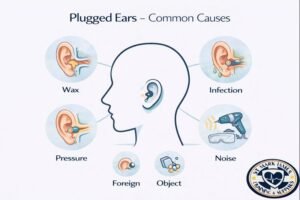
Identifying the underlying cause helps determine the right treatment.
1. Earwax Buildup
Earwax is produced naturally to protect the ear canal. Too much wax can lead to:
-
Fullness or pressure
-
Mild pain or irritation
-
Itching
-
Reduced or muffled hearing
Cotton swabs often push wax deeper, so professional removal is preferred.
2. Foreign Objects (More Common in Children)
Small toys, beads, seeds, and even bits of cotton from swabs can block the ear. Foreign bodies may cause swelling, discharge, or pain and should be removed safely by a clinician.
3. Ear Infections
After a cold or upper respiratory infection, the Eustachian tube (which equalizes pressure) may clog, leading to:
-
Plugged sensation
-
Popping or crackling
-
Fullness or pain
Fluid trapped in the middle ear is common in children and sometimes leads to acute infection. Ear infections may involve discharge if the eardrum is perforated.
4. Ear Growths
Certain benign growths can cause obstruction or reduced hearing:
-
Exostoses/osteomas: bony growths more common in frequent cold-water swimmers (“surfer’s ear”)
-
Otosclerosis: abnormal bone growth in the middle ear affecting sound conduction
These require medical assessment if symptoms progress.
5. Inner Ear Conditions
Inner ear disorders can affect hearing and balance. For example:
-
Menière’s disease can cause fullness, ringing, dizziness, and fluctuating hearing
-
Noise exposure (concerts, tools, machinery, gunfire) can temporarily or permanently affect hearing
Proper hearing protection is especially important in noisy workplaces across Canada.
6. Pressure & Altitude Changes
Air travel, diving, mountain driving, and rapid elevation changes can temporarily block the ears. Swallowing, yawning, or chewing gum usually helps equalize pressure.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Consult a healthcare provider if:
-
Symptoms last more than a few days
-
There is ear pain, discharge, or noticeable hearing decline
-
A child inserts an object into the ear
-
Symptoms follow loud noise or a blast
-
Dizziness or ringing accompany the blockage
Workplace & Prevention Context
Plugged ears and hearing issues are relevant in:
-
Construction & trades
-
Aviation & transportation
-
Manufacturing & industrial settings
-
Music & performance industries
Training in hearing protection, workplace safety, and first aid supports better prevention and early response across Canada.
Disclaimer
This post is for educational purposes only and not a substitute for assessment or diagnosis. Anyone with persistent hearing changes, worsening symptoms, or concerns about ear infection should seek medical care.
