Carotid Stenosis: Symptoms, Stroke Risk & When to Seek Emergency Care (Canada)
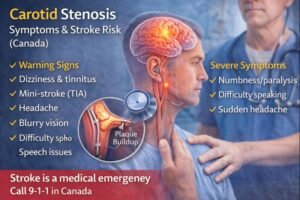
If blood and oxygen delivery become restricted, brain cells can become damaged or die, leading to stroke. Early recognition and medical assessment are critical.
Primary Symptoms & Warning Signs
Carotid stenosis may develop with no noticeable symptoms, which makes regular health screening important — especially for individuals with:
✔ High blood pressure
✔ High cholesterol
✔ Diabetes
✔ Smoking history
✔ Family history of vascular disease
A doctor may detect a bruit (a “whooshing” sound) in the carotid artery during a routine checkup using a stethoscope, prompting further vascular testing.
Possible Symptoms as the Condition Progresses
Some individuals may notice:
-
Dizziness or lightheadedness
-
Swishing sound in the ears (turbulent blood flow)
-
General fatigue or vague “off” feeling
Because symptoms can be subtle, carotid stenosis is often undiagnosed until a more serious event occurs.
Severe Symptoms: TIA (Mini-Stroke) or Stroke
In many cases, the first noticeable warning sign is a:
-
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) or
-
Full Ischemic Stroke
Both may include:
-
Numbness or paralysis on one side of the body
-
Sudden headache
-
Blurry or double vision
-
Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
-
Loss of coordination
A TIA is temporary and does not cause permanent damage, but it is a major warning sign of high stroke risk and requires urgent medical assessment.
Stroke is a medical emergency — call 9-1-1 immediately in Canada if symptoms appear.
Canadian First Aid / CPR & Workplace Safety Relevance
Recognizing stroke symptoms is a core component of Standard First Aid + CPR and Workplace First Aid training across Canada.
First responders and trained bystanders learn FAST assessment:
F — Face drooping
A — Arm weakness
S — Speech difficulty
T — Time to call 9-1-1
Early recognition and rapid EMS activation can dramatically improve stroke outcomes.
When to Seek Medical Care
A doctor should be consulted if:
✔ Symptoms are present, even if mild
✔ A TIA occurs (urgent)
✔ Risk factors are high
Regular blood pressure and cholesterol monitoring can significantly reduce stroke risk.
Training Opportunity (Canada)
Canadian workplaces and communities benefit from training that teaches:
✔ Stroke recognition
✔ EMS activation
✔ First responder communication
✔ CPR & AED basics (if cardiac arrest develops secondary to stroke)
If you’re in Canada and wish to upskill, consider Standard First Aid + CPR, Basic Life Support (BLS) or Workplace First Aid certification.
Medical Disclaimer (Canada)
This content is for general information only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you suspect a stroke, TIA, or medical emergency, call 9-1-1 immediately in Canada or seek urgent medical care.
