Biceps Muscle Injuries: Symptoms, First Aid Awareness & Workplace Relevance (Canada)
 What Is the Biceps Muscle?
What Is the Biceps Muscle?
The biceps is a two-headed muscle located at the front of the upper arm. It connects the shoulder region (scapula) to the forearm (radius) and is responsible for bending the elbow and rotating the forearm. It also contributes to lifting and carrying tasks, making it important in both daily activities and sports.
Why This Matters for First Aid & Workplaces
Biceps strains and tears can happen in workplaces that involve lifting, pulling, or repetitive motions, as well as in sports and recreation. Awareness helps people identify symptoms early, reduce discomfort, and seek healthcare assessment when needed.
Scenario: Mild & Realistic
During a warehouse shift, a worker lifted a heavy box and felt a sudden sharp discomfort in the upper arm along with noticeable weakness. The supervisor paused lifting duties, placed the arm in a sling for comfort, and arranged follow-up medical assessment. The worker later completed temporary modified duties while recovering.
How Biceps Injuries Happen
Biceps injuries can result from:
-
Heavy or sudden lifting
-
Forceful pulling or twisting
-
Falls or trauma to the arm
-
Weight training
-
Repetitive workplace tasks
Although biceps ruptures are more common in adults aged 40–60, they can occur at other ages, depending on workload and activity.
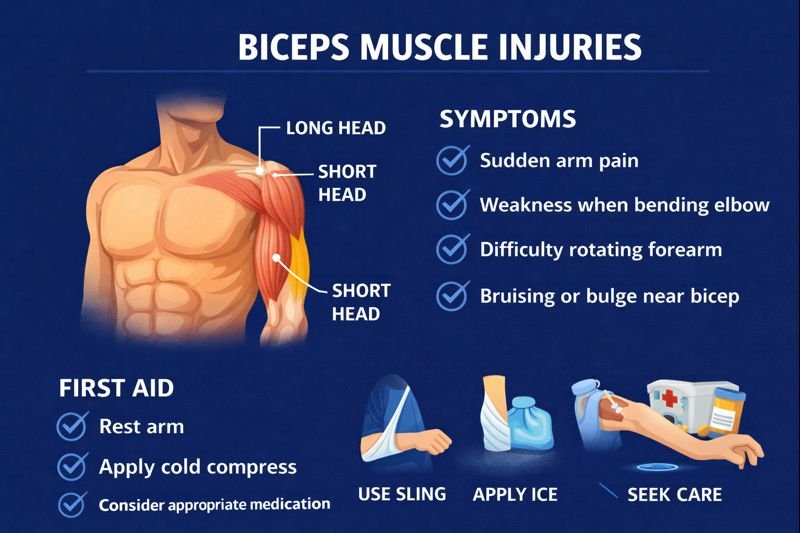
Symptoms of a Biceps Tear or Strain
Symptoms vary by severity, but individuals may notice:
-
Sudden upper arm pain
-
Weakness when bending the elbow
-
Difficulty rotating the forearm (palm-up motion)
-
Tenderness along the muscle
-
Visible change in muscle contour (sometimes described as a “bulge”)
-
Swelling or bruising
Healthcare assessment is important to determine the type and severity of injury.
First Aid Awareness & Immediate Considerations
Public first aid programs often emphasize:
-
Resting the arm and stopping the activity that caused pain
-
Supporting the arm comfortably using a sling
-
Applying a cold compress for short periods during the first day to reduce swelling
-
Avoiding heavy lifting or strenuous tasks
-
Seeking healthcare evaluation to confirm the injury and guide recovery
Healthcare professionals determine whether imaging, rehabilitation, or other interventions are needed.
Healthcare & Rehabilitation
Depending on the injury, healthcare professionals may:
-
Assess range of motion and strength
-
Recommend temporary activity modification
-
Provide physiotherapy programs to restore movement and strength
-
Monitor recovery over time
In some cases, particularly for athletes or individuals who require strong forearm rotation for work tasks, surgical repair may be recommended. Post-surgical care typically involves monitored rehabilitation.
Prevention & Workplace/Sports Considerations
-
Warm up before lifting or overhead activities
-
Use proper lifting mechanics
-
Rotate tasks to reduce repetitive strain
-
Report discomfort promptly in workplace settings
-
Balance upper-body training to reduce muscle imbalances
FAQ — Biceps Muscle Injuries
1. Do biceps tears always require surgery?
No. Treatment depends on severity, age, activity demands, and healthcare assessment.
2. Why is rotating the forearm difficult after injury?
The biceps contributes to supination (palm-up rotation), so weakness can be noticeable.
3. Can a tear happen suddenly?
Yes. Many individuals describe a sudden pulling sensation during lifting or sports.
4. Are workplace lifting tasks a factor?
They can be. Repetitive overhead or heavy lifting tasks may contribute to strain.
5. How long does recovery take?
Recovery time varies widely. Healthcare professionals guide rehabilitation based on the specific injury.
Educational Note
This article supports public awareness of biceps muscle injuries and when medical evaluation may help guide recovery. Healthcare professionals determine diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation plans.