Coliform Bacteria: Food and Water Safety Awareness in Canada
What Are Coliform Bacteria?
Coliform bacteria are a broad group of microorganisms commonly found in soil, water, and the digestive systems of humans and animals. Some types are harmless, but certain strains can contribute to gastrointestinal or urinary infections when people consume contaminated food or water or encounter poor hygiene conditions. Public education focuses on safe food handling, clean water practices, and early recognition of common symptoms.
Why Coliform Awareness Matters in Canadian Homes and Workplaces
In Canada, shared kitchens, food-service areas, childcare settings, outdoor recreation, and travel can all involve food and water handling. First aid awareness emphasizes hygiene, hydration, and preventing spread, rather than diagnosing illness. Clean preparation surfaces, proper cooking temperatures, and safe drinking water are key protective habits.
A Simple, Realistic Scenario
After a weekend camping trip, a family member develops stomach cramps and loose stools. Remembering basic food-safety guidance, they rest, increase fluid intake, and review handwashing and water-boiling practices for future trips.
Common Digestive Symptoms
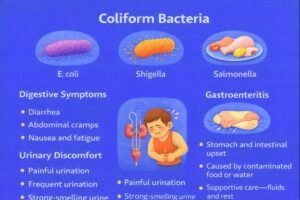
-
Abdominal cramps or tenderness
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Fever or chills
-
Fatigue and reduced appetite
Many mild cases improve with rest and fluids, but persistent or worsening symptoms should be checked further.
Urinary Tract Irritation
Some strains associated with the digestive tract can also contribute to urinary discomfort when hygiene practices are insufficient. Symptoms may involve:
-
Burning sensation during urination
-
Frequent urge to urinate
-
Lower abdominal discomfort
-
Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
General awareness focuses on hydration and hygiene, with further assessment encouraged if symptoms continue.
Gastroenteritis (Stomach and Intestinal Upset)
Gastroenteritis refers to irritation of the stomach and intestines, often linked to contaminated food or water. Typical features include diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain, and mild fever. Supportive care—especially fluids and rest—is central to first aid awareness.
Typhoid-Related Illness (Less Common in Canada)
Illness associated with Salmonella Typhi is uncommon in Canada but can occur during travel to areas with limited sanitation. Public-education messages highlight safe water consumption, hand hygiene, and food-safety precautions when travelling.
First Aid Awareness and General Supportive Measures
From a public-education perspective, the emphasis is on hydration, hygiene, and monitoring:
-
Encourage frequent sips of clean water or oral rehydration fluids
-
Rest and avoid strenuous activity while unwell
-
Wash hands thoroughly after washroom use and before food preparation
-
Clean and disinfect kitchen surfaces and utensils
-
Avoid preparing meals for others until symptoms clearly improve
-
Monitor for ongoing fever, weakness, or dehydration signs
First aid awareness supports comfort and cleanliness rather than medical treatment.
Prevention and Food-Safety Considerations in Canada
-
Cook meats, poultry, and eggs thoroughly
-
Keep raw foods separate from ready-to-eat items
-
Refrigerate leftovers promptly and reheat thoroughly
-
Use safe drinking water; boil or treat water when camping or travelling
-
Wash fruits and vegetables under clean running water
-
Practise regular handwashing with soap and water
These habits help reduce the likelihood of food- and water-borne illness at home, work, and community events.
Frequently Asked Questions About Coliform Bacteria
Are all coliform bacteria harmful?
No. Many are harmless, but some strains can cause digestive or urinary discomfort if hygiene or food safety is inadequate.
How does contamination usually occur?
Most often through improperly handled food, unsafe water, or unclean preparation surfaces.
Why is hydration emphasized?
Fluids help replace losses from diarrhea or vomiting and support overall recovery comfort.
Do outdoor activities increase risk?
Camping or travel can increase exposure if safe water and hand hygiene practices are not followed.
When should symptoms be checked further?
If fever is persistent, dehydration signs appear, or symptoms continue without improvement, further assessment is advisable.
Educational Note
This article is intended for general public and workplace education in Canada. It supports food- and water-safety awareness and first aid recognition but does not replace evaluation or care from qualified healthcare professionals.
