Bruised Ribs: Causes, Symptoms & First Aid Care (Canada)
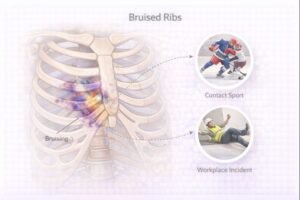
Because rib movement is tied to breathing, bruising in this area can be particularly uncomfortable. Pain typically increases with deep breaths, coughing, sneezing, laughing, or twisting movements.
Signs & Symptoms
Common symptoms of rib bruising include:
-
Localized pain in the chest or upper abdomen
-
Pain that worsens with movement or deep breathing
-
Sensitivity to touch over the affected ribs
-
Minor swelling or bruising of the skin (not always visible)
In most cases, bruised ribs heal on their own within several weeks.
Causes & Risk Factors
Bruised ribs can result from:
-
Contact sports (e.g., hockey, football, rugby)
-
Falls or blunt-force impact
-
Motor-vehicle collisions
-
Workplace injuries involving slips, impact or forceful movement
-
Physical altercations
Athletes and workers in environments with higher physical demands have increased risk, reinforcing the importance of injury prevention, PPE use, and onsite first aid awareness.
First Aid Care & Home Management
Compression
A rib binder or elastic bandage may be used to provide gentle support and limit abrupt movements. It should never be applied too tightly, as this can restrict healthy breathing. Compression products are widely available in pharmacies across Canada.
Cold Therapy
Applying a cold pack for 10–15 minutes at a time can help reduce swelling and discomfort, especially during the first 48–72 hours. Always use a towel barrier to protect the skin.
Pain Management
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen may be used if appropriate for the individual. Follow the dosing instructions on the packaging and consult a healthcare provider if unsure.
Activity Modification
Avoid heavy lifting, twisting, or strenuous movement until pain improves. Light movement such as ankle pumps or short walks can support circulation during recovery.
Nutrition & Hydration
When individuals become less active due to pain, constipation can develop. Increased fibre intake (fruits, vegetables, whole grains) and staying well-hydrated can help reduce strain on the abdominal region.
When to Seek Medical Care
Although bruised ribs are usually mild, medical assessment is recommended if:
-
Pain persists or worsens over time
-
Breathing becomes difficult
-
There is visible deformity or suspected fracture
-
Pain is accompanied by dizziness, coughing blood, fever, or shortness of breath
In rare cases, deep chest trauma can lead to complications such as pneumonia, especially in older adults or individuals with respiratory conditions.
Prevention & Workplace Relevance (Canada)
In Canadian workplaces, risk reduction may include:
-
Protective gear for workers in high-impact or physical roles
-
Slip-prevention and ergonomic programs
-
First aid and incident-response readiness
-
Encouraging early reporting of injuries
For athletes, proper equipment, safe return-to-play practices, and warm-up conditioning remain key.
Educational Use Disclaimer
This article is intended for public education and general first aid awareness in Canada. It is not a medical diagnosis or treatment guide. Always consult a healthcare professional for personal medical concerns or emergencies.
