Small Vessel Disease of the Brain — What to Know (Canada)
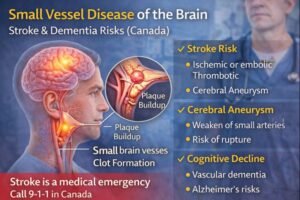
Small vessel disease is medically significant because it increases the risk of:
-
Stroke (ischemic)
-
Cerebral aneurysm
-
Thrombotic/embolic events
-
Cognitive decline and dementia
Stroke Risk
Cholesterol deposits can contribute to the formation of small clots within brain vessels. These clots may block blood flow, triggering ischemic stroke. In other cases, fragments break off and travel, causing an embolic or thrombotic stroke.
In Canada, stroke is considered a medical emergency requiring immediate activation of 9-1-1.
Cerebral Aneurysm
Atherosclerosis (plaque buildup) can weaken small arteries in the brain. A weakened section may balloon outward to form an aneurysm, which may:
-
cause pressure on brain structures
-
rupture and lead to hemorrhagic stroke
Both scenarios require emergency medical care.
Cognitive Decline & Alzheimer’s Disease
Small vessel blockages can injure brain tissue over time. Emboli and microclots can produce small lesions that contribute to vascular dementia. In some individuals, this process may worsen Alzheimer’s disease due to impaired blood–brain exchange and amyloid plaque accumulation.
Canadian First Aid & CPR Relevance
Stroke and aneurysm emergencies are time-critical. CPR and First Aid training in Canada teaches participants how to:
-
identify signs of stroke (FAST/BE FAST models)
-
activate EMS (9-1-1) promptly
-
support an individual until paramedics take over
-
monitor airway and breathing if the person becomes unresponsive
This is particularly important in workplaces, community settings, and recreation facilities where sudden neurological emergencies may occur.
When to Seek Medical Care
Consult a healthcare provider if symptoms such as dizziness, visual changes, speech difficulty, sudden headaches, or transient weakness occur. These can be warning signs of transient ischemic attacks (TIAs).
Canadian Emergency Reminder
If stroke symptoms appear, call 9-1-1 immediately.
Disclaimer
This content is for general information only and does not replace medical advice. If you suspect a stroke or neurological emergency, call 9-1-1 in Canada. For workplace medical response capabilities, consider certified First Aid & CPR training.
