Pelvic Muscle Pain: Symptoms, Causes & First Aid Awareness (Canada)
 What Are the Pelvic Muscles?
What Are the Pelvic Muscles?
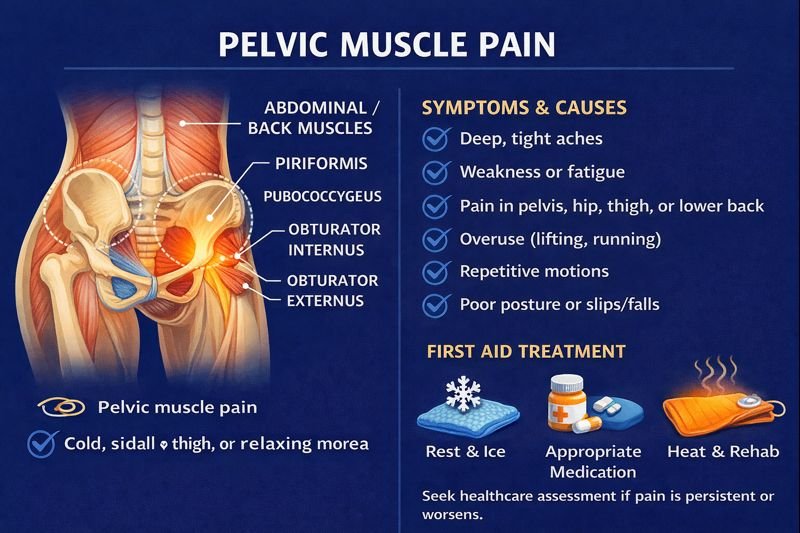
Pelvic muscles include deep muscles located inside the pelvic region and external muscles that attach to the hips, thighs, abdomen, and lower back. These muscles support posture, movement, lifting, walking, and balance. Because many muscle groups attach to or pass near the pelvis, discomfort can be felt in several areas, including the hip, lower back, abdomen, or upper thigh.
Why This Matters for First Aid & Workplaces
Pelvic and hip discomfort can affect mobility, lifting, and daily tasks. Canadians may encounter pelvic muscle pain from sports, repetitive motions, slips and falls, or prolonged sitting or standing. Pelvic muscle pain awareness helps identify when rest, activity modification, or healthcare assessment may be beneficial.
Scenario: Mild & Realistic
A recreational runner developed tightness around the hips after increasing mileage. They paused training, used gentle stretching, rested for a few days, and later adjusted running volume based on advice from a physiotherapist.
How Pelvic Muscle Pain Presents
Pelvic muscle pain may arise from:
-
Overuse or repetitive movements
-
Poor posture or prolonged sitting
-
Reduced flexibility
-
Lower back involvement
-
Tight hip or thigh muscles
Pain may feel:
-
Tight
-
Achy
-
Weak or fatigued
-
Radiating toward hip, thigh, or lower back
Some people notice variations throughout the day, especially with movement or prolonged positions.
Additional Considerations
Pelvic discomfort is complex, and not all pain is muscular. Healthcare professionals consider other possible sources, such as:
-
Hip joint conditions
-
Lower spine issues
-
Internal organ discomfort
-
Bladder or reproductive system concerns (common in women)
-
Nerve-related pain
Because multiple structures share similar nerve pathways, healthcare assessment can help determine contributing factors.
First Aid Awareness: Ice, Heat & Rest
Public first aid programs often highlight:
-
Rest to reduce irritation and prevent further strain
-
Cold packs early after a suspected strain to reduce swelling
-
Heat later on to relax tense or tired muscles once swelling settles
Cold and heat should be comfortable and applied with barriers to protect the skin. Persistent swelling, pain, or numbness warrants professional evaluation.
Rehabilitation & Recovery
Healthcare professionals may:
-
Assess for biomechanical or muscular imbalances
-
Use stretching and strengthening programs
-
Incorporate physiotherapy or guided exercise
-
Address posture, gait, or sport technique
-
Recommend gradual return to activity
Massage and certain pain-modulating therapies (e.g., physiotherapy modalities or TENS) may be part of broader rehabilitation under clinical supervision.
Healing Time
Recovery varies widely. Mild muscle strains from sports or workplace activity may resolve over weeks, while more significant strains can take longer. Consistency with rest, guided movement, and gradual return-to-activity supports recovery.
Prevention & Workplace/Sports Considerations
-
Warm up before physical tasks or sports
-
Rotate duties to avoid overuse
-
Maintain hip, core, and lower-back strength
-
Incorporate flexibility training
-
Use ergonomics for lifting or prolonged sitting
-
Report workplace discomfort early for modifications
FAQ — Pelvic Muscle Pain
1. Can pelvic muscle pain be confused with other conditions?
Yes. The pelvis is influenced by muscles, joints, and organs, so healthcare professionals may assess multiple structures.
2. Do pelvic muscle strains only affect athletes?
No. They can occur during daily lifting, slips, sitting for long periods, or repetitive workplace tasks.
3. Does stretching help pelvic mobility?
Stretching and strengthening are often part of rehabilitation but should be guided by a professional if pain persists.
4. How long does pelvic muscle pain last?
Recovery timelines vary widely. Mild strains may improve quickly; more complex cases can take months.
5. When should someone seek medical assessment?
If pain is persistent, unusual, worsening, or affects bladder/bowel function, mobility, or daily tasks, healthcare evaluation is useful.
Educational Note
This article supports public awareness of pelvic muscle pain, workplace ergonomics, and first aid considerations. Healthcare professionals determine diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation plans.