Medial Ligament (MCL) Sprain: Knee Injury Awareness and First Aid
A medial ligament sprain—often referred to as an MCL sprain—involves damage to the ligament located on the inner (medial) side of the knee. This ligament helps stabilize the knee against inward forces. Injuries typically occur due to twisting movements, sudden changes in direction, or direct impact to the outside of the knee.
Medial ligament sprains are common in contact sports such as football, rugby, hockey, and martial arts, but they can also occur from falls or awkward movements during everyday activities.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the severity of the injury but often include:
- Pain or tenderness along the inner side of the knee
- Swelling near the ligament (may be mild or moderate)
- Pain when bending or bearing weight
- A feeling of instability or looseness in the knee
- Difficulty changing direction or pivoting
In more severe cases, the knee may feel unstable or “wobbly.”
Understanding Injury Severity
Medial ligament sprains are commonly described in three grades:
Grade 1 (Mild)
- Minor stretching or small tears in the ligament
- Localized tenderness on the inner knee
- Little to no swelling
- Knee remains stable, though movement may be painful
Grade 2 (Moderate)
- Partial tear of the ligament
- Noticeable tenderness and swelling
- Pain and some looseness when the knee is stressed
- Walking and activity may be difficult
Grade 3 (Severe)
- Complete tear of the ligament
- Knee instability or giving way
- Swelling may be present
- Pain can vary and may feel less intense than a grade 2 injury
First Aid and Initial Care
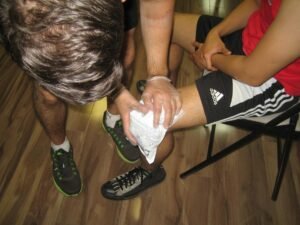
Early care focuses on protecting the knee and limiting further injury. First aid principles commonly include:
- Protection and rest: Avoid activities that increase pain or instability
- Cold application: Apply an ice pack for short intervals to reduce pain and swelling
- Compression: Use a light wrap or knee support if advised
- Elevation: Elevating the leg may help manage swelling
Anyone with a suspected ligament injury should limit activity and seek medical assessment, especially if instability is present.
Recovery and Support
Depending on severity, a brace or support may be used to limit sideways movement and protect the ligament while healing. Once pain and swelling improve, rehabilitation often focuses on restoring strength, balance, and mobility under professional guidance.
Early recognition and proper management can reduce the risk of long-term knee instability or repeat injury.
Why First Aid Training Matters
Knee ligament injuries are common in sports, workplaces, and recreational activities across Canada. First aid training helps individuals recognize joint injuries, provide appropriate early care, and understand when medical evaluation is necessary.
This knowledge supports safer participation in physical activity and quicker response to injuries when they occur.
Educational Disclaimer
This content is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. To learn how to recognize and respond to joint and ligament injuries, consider enrolling in a first aid and CPR course with a Canadian training provider.
