Herniated (Slipped) Disc: Symptoms, Causes, and First Aid Awareness in Canada
What Is a Herniated Disc?
A herniated disc, sometimes called a slipped disc, most commonly affects the lower back (lumbar spine). It is one of the leading causes of low back pain and leg pain. Many people in Canada will experience back pain at some point in their lives, and a herniated disc is a frequent underlying reason.
Although symptoms can be uncomfortable, most people improve over time without surgery, especially with early awareness, activity modification, and conservative care.
First Aid and Workplace Relevance in Canada
Herniated discs are relevant in Canadian workplaces involving lifting, bending, twisting, prolonged sitting, or repetitive movements—such as construction, warehousing, transportation, healthcare, and office settings.
First aid and injury-awareness training helps individuals recognize nerve-related back pain, respond appropriately, and avoid actions that may worsen symptoms while recovery takes place.
A Simple, Realistic Scenario
An office worker develops low back pain after several weeks of long hours at a workstation. A few days later, the pain improves but is replaced by a sharp ache running down one leg. Remembering first aid education, they adjust posture, take movement breaks, and seek medical assessment when leg symptoms persist.
What Happens During a Herniated Disc?
Spinal discs act as shock absorbers between the bones of the spine. Each disc has:
-
A soft, jelly-like centre (nucleus)
-
A tougher outer ring
A herniated disc occurs when the inner material pushes against or through the outer ring due to wear and tear or sudden strain. This can irritate nearby spinal nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness—often felt in the leg rather than the back.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Most herniated discs are related to natural aging of the spine.
Contributing factors include:
-
Disc degeneration over time
-
Reduced disc hydration and flexibility
-
Repetitive lifting or twisting
-
Sudden awkward movements
-
Prolonged sitting or poor posture
As discs age, they shrink and weaken, narrowing the space between vertebrae and making them more prone to injury.
Symptoms to Watch For
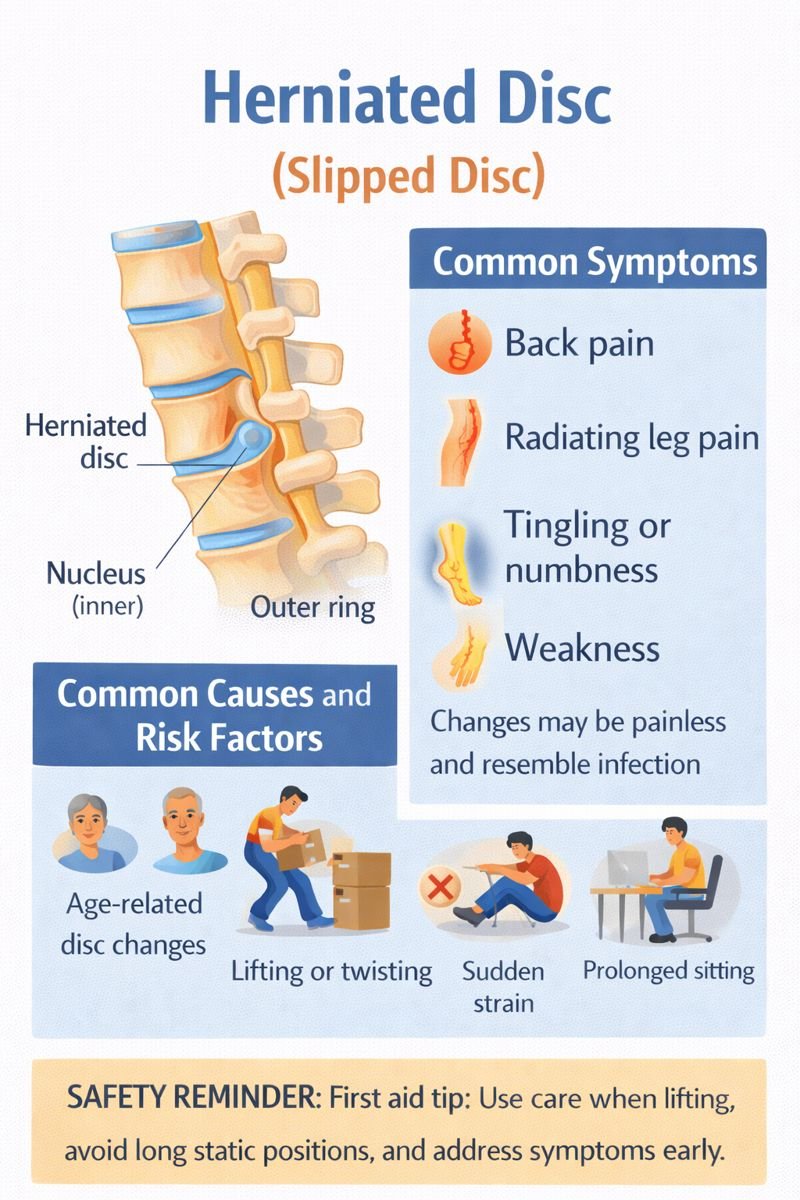
Common symptoms include:
-
Low back pain (often the first symptom)
-
Pain radiating from the back or buttock down one leg
-
Pain extending below the knee into the foot or ankle
-
Tingling or numbness in the leg or foot
-
Weakness in the leg or foot
In some cases, changes in bowel or bladder control may occur and require urgent medical assessment.
Not everyone experiences pain during disc degeneration, which can make diagnosis challenging.
First Aid and Early Management
From a first aid perspective, early care focuses on protecting the spine and avoiding further irritation.
General first aid considerations may include:
-
Avoiding sudden movements and heavy lifting
-
Changing positions regularly rather than prolonged sitting
-
Using controlled, gentle movement
-
Allowing brief rest during severe pain episodes
Most people experience gradual improvement within weeks to months.
Treatment and Recovery Expectations
The majority of lower back herniated discs improve with non-surgical care. Many individuals feel significantly better within 3 to 4 months, although flare-ups may occur during recovery.
Medical professionals may recommend a combination of activity modification, guided exercise, and symptom management strategies based on individual needs.
Prevention and Workplace Safety Tips
Reducing the risk of herniated disc injuries includes:
-
Using proper lifting techniques
-
Strengthening core and back muscles
-
Maintaining good posture at workstations
-
Taking regular movement breaks
-
Avoiding prolonged static positions
Early reporting of back and leg symptoms in the workplace can help prevent long-term issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does a herniated disc always cause back pain?
No. Some people experience leg pain or numbness without significant back pain.
Why does leg pain increase when back pain improves?
As the disc material irritates spinal nerves, symptoms may shift from the back to the leg.
Do all herniated discs require surgery?
Most cases improve with conservative, non-surgical care.
Can a herniated disc heal over time?
Yes. Many people recover gradually as inflammation settles and the body adapts.
How does first aid training help with back injuries?
First aid education promotes early recognition, safe movement, and timely medical follow-up.
Educational Note
This article is intended for general public education and workplace first aid awareness in Canada. It does not replace medical assessment, diagnosis, or individualized treatment for back or nerve-related conditions.
