Broken Fibula: Causes, Treatment Options, and Recovery
Treatment depends on the injury pattern, severity, and whether bone fragments have shifted out of alignment.
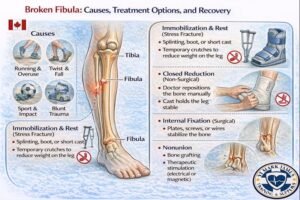
Causes and Injury Patterns
Fibula fractures can result from:
-
Running and repetitive impact (stress fractures)
-
Twisting ankle injuries
-
Contact sports or falls
-
Blunt trauma or accidents
Stress fractures tend to occur gradually due to repetitive loading, while acute fractures develop suddenly after an impact or twist.
Immobilization and Rest (Stress Fractures)
Stress fractures of the fibula are commonly seen in runners, jumpers, and active individuals. These fractures often occur near the ankle but can also appear near the knee in impact sports.
Management may involve:
-
Splinting or casting
-
Short-term crutch use to reduce pain with walking
-
Gradual return to activity once discomfort improves
-
Medical supervision to ensure full healing
Closed Reduction (Non-Surgical Realignment)
If the bone pieces remain close to normal alignment, a physician may reposition them manually. Afterward, a cast or boot helps keep the leg stable during healing. Because the fibula contributes to ankle stability, weight-bearing status may vary depending on the fracture and provider guidance.
Internal Fixation (Surgical Stabilization)
More complex fractures may require surgery to realign and secure the bone using:
-
Plates and screws
-
Flexible wires (e.g., K-wires)
-
Other fixation hardware
These devices keep the fragments stable so they can heal properly.
Nonunion (Delayed or Incomplete Healing)
In some cases, a fractured fibula may not heal fully, a condition called nonunion. This is more likely at the lower end of the bone where blood flow is limited. Management options include:
-
Conservative therapies such as electrical or magnetic bone stimulation
-
Surgical stabilization or bone grafting to encourage healing
Workplace and Safety Considerations
Fibula fractures are common in both recreational sport and occupational environments. Workplaces with slip hazards, uneven surfaces, manual handling, or ladder use see a higher risk of lower-leg injuries. Preventative strategies overlap with broader Canadian safety education programs including:
-
First aid and injury management training
-
Workplace safety and PPE programs
-
CPR/AED certification for emergency response preparedness
-
Sports and recreation first aid for coaches and community groups
Disclaimer
This post is for public education only and not a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Canadians experiencing fractures or mobility issues should seek care from a qualified healthcare professional.
