Lower Back Muscle Strain: Symptoms, Severity, and First Aid Awareness in Canada
What Is a Lower Back Muscle Strain?
A lower back muscle strain occurs when the muscles or tendons in the lower back are overstretched or torn. These injuries can happen suddenly or develop gradually over time. The lower back is particularly vulnerable because it supports body weight and is involved in lifting, twisting, and prolonged postures.
Proper early care is important. If back muscle strains are not managed well, muscle imbalances and recurring pain may develop later.
First Aid and Workplace Relevance in Canada
Lower back muscle strains are among the most common injuries in Canadian workplaces, especially in jobs involving lifting, manual handling, prolonged sitting, or repetitive movements. They are also common in sports, fitness activities, and everyday household tasks.
First aid awareness helps individuals recognize strain severity, modify activity early, and reduce the risk of long-term back issues.
A Simple, Realistic Scenario
A warehouse worker feels a sharp pain in their lower back while lifting a box with poor posture. Movement becomes difficult, and stiffness sets in over the next few hours. Remembering first aid training, they stop lifting, apply cold therapy, and rest rather than pushing through the pain.
Common Symptoms of Lower Back Muscle Strain
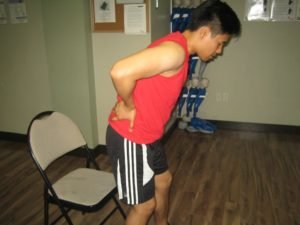
Symptoms vary depending on how severe the strain is but may include:
-
Sudden sharp or stabbing pain in the lower back
-
Swelling or bruising over the injured area
-
Difficulty bending, twisting, or standing upright
-
Pain that worsens with movement
Direct impact to the lower back—especially near bone—should be managed carefully, as it may involve bruising or deeper injury.
Understanding Muscle Strain Severity
Lower back muscle strains are commonly grouped into three grades based on severity.
Grade 1 (Mild Strain)
-
Tightness or soreness in the lower back
-
Minimal swelling
-
Walking and daily movement usually possible
-
Pain may be present but manageable
Grade 2 (Moderate Strain)
-
More noticeable pain and stiffness
-
Difficulty walking or moving normally
-
Swelling and tenderness over the injury site
-
Pain triggered when the area is pressed or during activity
Grade 3 (Severe Strain)
-
Severe pain with immediate swelling
-
Significant difficulty or inability to walk normally
-
Pain when muscles contract
-
Possible visible bulge in the muscle
-
Recovery may take weeks to months
Causes of Lower Back Muscle Strain
Lower back muscle strains may occur due to:
-
Sudden or awkward movements
-
Lifting heavy objects improperly
-
Poor posture over time
-
Repetitive overuse
-
Muscle fatigue or weakness
In many cases, low back pain develops gradually, as muscles tighten and fatigue due to ongoing strain. Reduced blood flow to tight muscles can lead to spasms and weakness, increasing the risk of injury.
First Aid and Early Management
From a first aid perspective, early care focuses on protecting the injured muscles and reducing pain.
General first aid considerations include:
-
Stopping activities that worsen pain
-
Using cold therapy during the early phase
-
Supporting the lower back during movement
-
Avoiding sudden bending or lifting
Early recognition and rest help prevent worsening of the injury.
Management Based on Severity
Management approaches vary depending on strain grade.
Mild strains often improve with:
-
Short-term activity reduction
-
Avoiding painful movements
-
Gradual return to normal activities
Moderate to severe strains may require:
-
Longer rest from aggravating activity
-
Structured rehabilitation to restore strength and flexibility
-
Guided progression back to work or sport
Medical assessment is important if pain is severe, persistent, or worsening.
Prevention and Workplace Back Safety
Reducing the risk of lower back strains includes:
-
Using proper lifting techniques
-
Maintaining good posture
-
Strengthening core and back muscles
-
Taking breaks during repetitive tasks
-
Reporting early signs of back discomfort
Workplace ergonomics and task modification play a key role in prevention.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can lower back muscle strains develop gradually?
Yes. Poor posture and overuse can cause slow muscle tightening that leads to strain.
Are all back strains caused by lifting?
No. Sudden movements, overuse, or fatigue can also cause strains.
Why does back pain sometimes feel worse after resting?
Muscle stiffness can increase after inactivity, especially early in recovery.
How long does recovery take?
Recovery depends on severity and can range from days to several weeks or longer.
How does first aid training help with back injuries?
First aid education promotes early recognition, rest, and safe activity modification.
Educational Note
This article is intended for general public education and workplace first aid awareness in Canada. It does not replace medical assessment, diagnosis, or individualized treatment for back injuries.
