Understanding Bullous Myringitis (Infected Eardrum) in Children
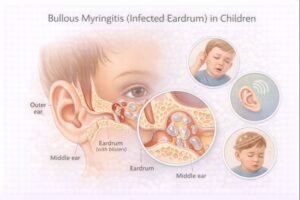
While most infections improve with proper care, untreated cases may lead to hearing concerns or other complications. For this reason, parents and caregivers should recognize the symptoms and know when to seek medical assessment.
Common Signs & Symptoms
Ear pain (otalgia) is one of the most noticeable symptoms, especially in school-aged children and teens. Younger children—particularly those under two—may not verbalize pain and instead show behaviour such as:
• ear tugging or rubbing
• irritability
• difficulty sleeping or feeding
Hearing Changes
Hearing loss can occur temporarily when fluid builds up behind the eardrum. This pressure causes the eardrum to bulge outward, interfering with sound transmission. The hearing loss is often described as muffled, similar to wearing earplugs, and usually improves once the fluid drains.
Dizziness or Vertigo
Some children experience dizziness or vertigo. The inner ear helps control balance, and because the middle and inner ear sit close together, inflammation can irritate nearby structures.
Associated Infection
Bullous myringitis may accompany or follow a respiratory infection. Fever, irritability, or general fatigue can also be present depending on the cause.
When to Seek Care
Parents and caregivers should consult a healthcare provider if a child has:
• persistent ear pain
• hearing difficulty
• fever with ear symptoms
• fluid or drainage from the ear
• balance concerns
• symptoms lasting longer than 48–72 hours
Early assessment helps prevent complications and ensures the correct treatment, which may include pain management or antibiotics depending on the cause.
Workplace Safety & First Aid Training Relevance (Canadian Context)
While bullous myringitis is a medical condition managed by clinicians, first aid education helps Canadians recognize when symptoms require medical attention, especially in childcare settings, schools, sports environments, and workplaces where children are present.
Across Canada, First Aid and CPR training standards emphasize:
• early recognition of illness or infection
• monitoring for worsening symptoms
• knowing when to seek emergency vs. non-urgent care
• supporting safe return-to-activity for children
Understanding conditions like ear infections also supports effective communication between caregivers and healthcare professionals—skills reinforced in nationally recognized workplace and first aid training programs.
Disclaimer (Educational Only)
This information is provided for learning and awareness purposes and is not a clinical diagnosis or medical treatment guide. Any suspected ear infection or hearing change should be assessed by a qualified healthcare professional, especially in children.
