Peripheral Neuropathy: Early Symptoms, Safety Considerations, and When to Seek Care
Common causes include diabetes, metabolic disorders, chronic infections, toxin exposure, certain medications, autoimmune conditions, and injuries. While neuropathy is not typically a first aid emergency, early recognition and monitoring help prevent complications—especially foot wounds that may go unnoticed due to numbness.
In Canada, peripheral neuropathy is frequently linked to poorly controlled diabetes. Regular medical follow-up, healthy lifestyle habits, and awareness of foot care are encouraged to prevent secondary complications such as ulcers and infection.
Common Early Symptoms
Nerve Pain
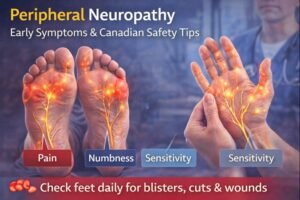
Pain is often the first noticeable symptom. Individuals describe it as burning, stabbing, electric-like, or shooting. Foot pain often appears before hand symptoms.
Prompt medical evaluation is important—especially if the pain is new, worsening, or unexplained. Early treatment of underlying causes can slow progression and reduce long-term nerve damage.
Numbness
Numbness results from impaired sensory nerve function and may limit perception of heat, touch, pressure, or pain.
Because numbness can mask injuries, individuals should routinely check feet for:
-
Blisters
-
Cuts
-
Pressure areas
-
Dry or cracked skin
If wounds are missed or untreated, they may become infected, which can lead to serious complications—particularly for those with diabetes.
Sensitivity to Touch
Some individuals experience heightened sensitivity to even mild touch. This symptom can interfere with daily activities and sleep due to discomfort.
A healthcare provider can determine the cause and offer management options including medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments.
Self-Care and Safety Measures
Management often involves treating the root cause. In addition, individuals may be advised to:
-
Exercise regularly (as tolerated)
-
Maintain healthy blood sugar levels
-
Avoid prolonged pressure on feet and hands
-
Stop smoking (supports circulation)
-
Eat balanced meals
-
Inspect feet and hands daily
These habits help reduce complications and support overall nerve health.
When Does Neuropathy Connect to First Aid Training?
While neuropathy itself isn’t a first aid emergency, related complications can become relevant in workplace and community settings. For example:
-
Numbness may prevent detection of burns or cuts
-
Reduced sensation increases infection risk
-
Foot wounds may require basic wound care skills
Canadian first aid training teaches participants how to recognize when an injury requires monitoring, dressing, or medical referral—useful knowledge for workplaces where chronic health conditions are common.
Educational Disclaimer
This information is for learning and general awareness only. It is not a diagnosis or medical treatment plan. Anyone experiencing new, persistent, or worsening symptoms should seek assessment from a qualified healthcare provider in Canada.
