Hepatitis A and Hepatitis C: Understanding Liver Inflammation, Transmission, and Prevention in Canada
What Is Hepatitis?
Hepatitis is a condition involving inflammation of the liver, an organ essential for digestion, energy storage, and filtering harmful substances from the body. Worldwide, hepatitis is a leading cause of liver disease. Several viruses can cause hepatitis, including hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. While these infections can share similar symptoms, some forms are short-term, while others can become long-lasting and lead to serious health complications.
This article focuses on hepatitis A and hepatitis C, two of the more commonly discussed types in public health and workplace safety education.
First Aid and Workplace Relevance in Canada
In Canadian workplaces—especially those involving food handling, healthcare, travel, or community services—awareness of hepatitis is important. Hepatitis A can spread through contaminated food or water, making hygiene and sanitation critical in many work environments. Hepatitis C, while not spread through casual contact, is a concern in healthcare and first aid contexts where blood exposure may occur.
Understanding how hepatitis spreads, recognizing early symptoms, and following basic first aid and infection prevention practices can help reduce risk and support safer workplaces.
A Simple, Realistic Scenario
During a busy shift at a community centre, a staff member notices a colleague feeling unusually fatigued and nauseated, with a yellowish tinge in their eyes. Remembering their workplace first aid training, the staff member encourages the colleague to rest, avoid food handling duties for the day, and seek medical assessment. The situation is handled calmly, and hygiene protocols are reinforced to reduce any potential risk to others.
Symptoms of Hepatitis A and C
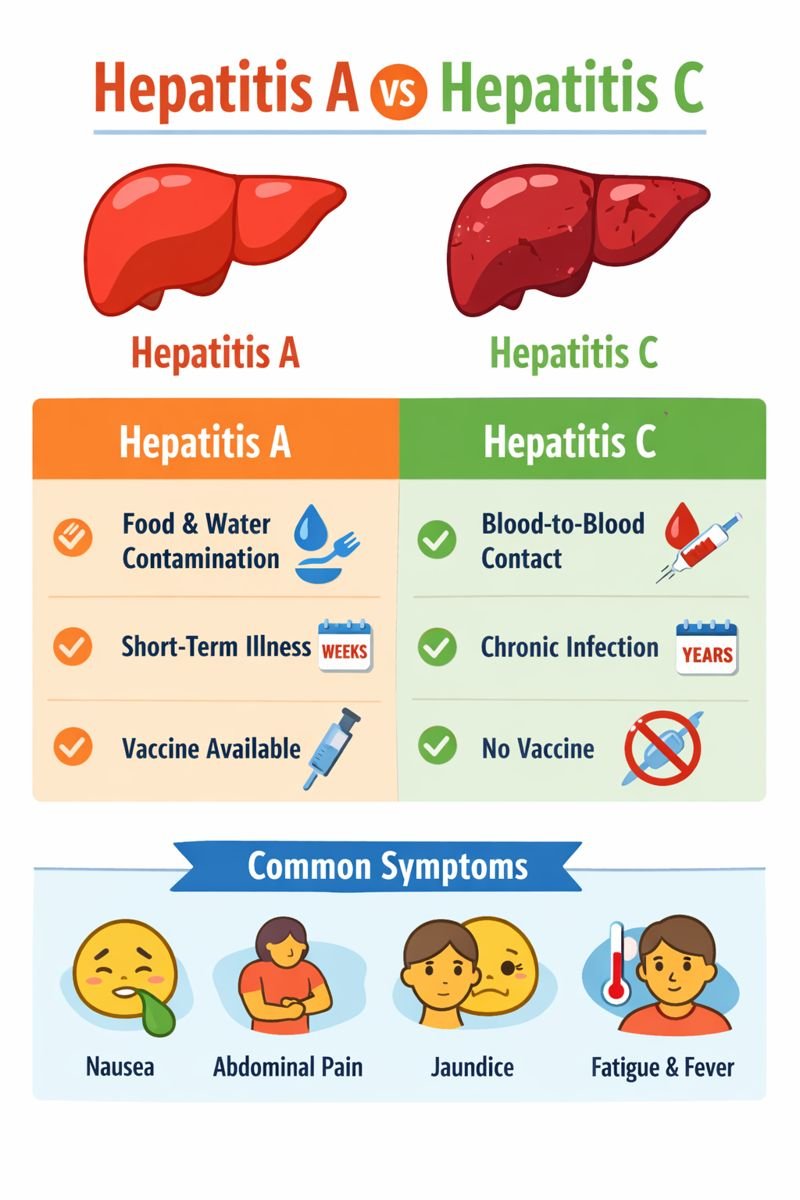
Common symptoms include:
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Abdominal discomfort or pain
-
Loss of appetite
-
Fever
-
Fatigue
-
Joint pain
-
Pale or gray-coloured stools
-
Yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice)
Hepatitis A typically has an incubation period of 15 to 50 days, with symptoms often appearing around four weeks after exposure. Hepatitis C has a broader incubation range of about 14 to 80 days, and many people may have mild or unnoticed symptoms in the early stages.
Causes and How These Viruses Spread
Hepatitis A is most commonly spread through:
-
Consuming food or water contaminated with fecal matter
-
Poor hand hygiene
-
Close personal or sexual contact with someone who is infected
People may be at higher risk when travelling to areas with limited sanitation or during foodborne outbreaks.
Hepatitis C spreads through blood-to-blood contact, including:
-
Sharing needles or other injection equipment
-
Accidental exposure to blood in healthcare or first aid settings
-
From an infected parent to an infant during birth
-
Less commonly, through sexual contact
In some cases, the exact source of hepatitis C infection is not identified.
Management and First Aid Considerations
There is no specific cure for hepatitis A. Management focuses on:
-
Supporting hydration if vomiting or diarrhea occur
-
Rest and gradual return to normal activities
-
Monitoring symptoms until recovery
Most people recover fully from hepatitis A within weeks or months, and it does not become a long-term condition.
Hepatitis C may begin as a short-term infection, but if it lasts longer than six months, it is considered chronic. Chronic hepatitis C can lead to ongoing liver inflammation and complications over time. Management generally involves medical monitoring and, in some cases, antiviral therapies directed by healthcare professionals.
From a first aid and workplace perspective, the focus is on infection prevention, safe handling of blood or bodily fluids, and encouraging appropriate medical follow-up.
Prevention and Workplace Considerations
Preventing hepatitis relies heavily on education and hygiene practices.
Key prevention measures include:
-
Regular handwashing, especially before food preparation
-
Safe food handling and sanitation practices
-
Using protective barriers when there is a risk of blood exposure
-
Following workplace infection control policies
A vaccine is available for hepatitis A and is commonly recommended for individuals at higher risk, including certain travellers and workers. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C, making prevention through safe practices especially important.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can hepatitis spread through casual contact at work?
Hepatitis A can spread through poor hygiene and contaminated food, but hepatitis C does not spread through casual contact such as handshakes or sharing office space.
Why is hepatitis A often linked to food safety?
Hepatitis A is transmitted through the fecal-oral route, which means improper handwashing or contaminated food and water can play a role in outbreaks.
Do all people with hepatitis have symptoms?
No. Some individuals, especially those with hepatitis C, may have mild or no noticeable symptoms for long periods.
Why is hepatitis C considered more serious over time?
Hepatitis C can become chronic and cause long-term liver inflammation, which may lead to complications if not monitored.
How does first aid training help with hepatitis awareness?
First aid training emphasizes infection prevention, safe handling of bodily fluids, and early recognition of symptoms that should be medically assessed.
Educational Note
This article is intended for general public education and workplace first aid awareness in Canada. It does not replace professional medical assessment, diagnosis, or individualized care.
