Food Poisoning: Symptoms, First Aid Awareness, and Workplace Safety in Canada
 Understanding Food Poisoning
Understanding Food Poisoning
Food poisoning occurs when a person eats food or drinks beverages contaminated with harmful bacteria, viruses, parasites, or toxins. Contamination can happen at many stages — during food production, transportation, storage, or preparation. While many people recover on their own within a short time, some cases can lead to dehydration or other complications, making awareness and early response important.
First Aid & Workplace Relevance in Canada
In Canadian workplaces, food safety is closely tied to overall occupational health. Shared kitchens, catered meetings, staff barbecues, and community events can increase the risk of improper food handling or temperature control. Basic first aid awareness helps coworkers recognize early digestive symptoms, encourage hydration, and support safe food practices such as handwashing, refrigeration, and proper reheating.
A Short Realistic Scenario
At a workplace potluck, an employee begins to feel nauseated and develops stomach cramps later that afternoon. A colleague with first aid awareness suggests resting, sipping water, and avoiding further food until symptoms settle. The employee monitors their condition and later decides to seek professional advice because the symptoms continue into the next day. The calm response and early hydration help prevent worsening discomfort.
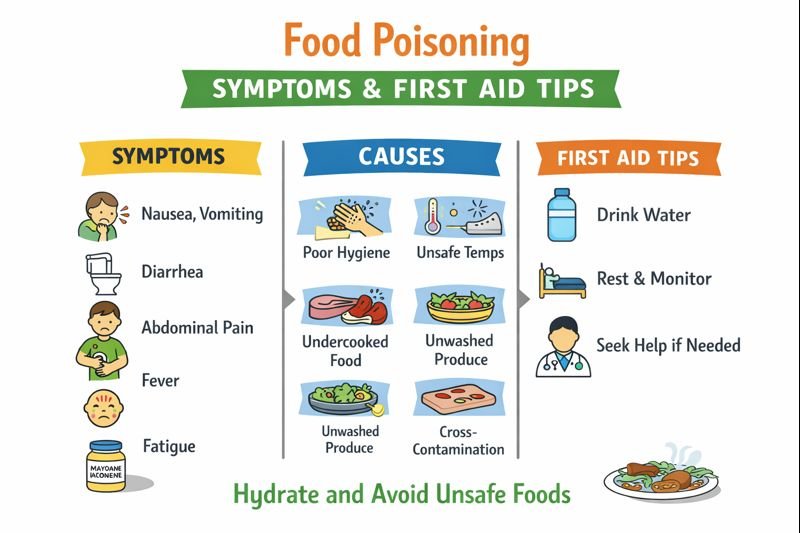
Common Symptoms
Food poisoning symptoms often affect the digestive system and may include:
-
Nausea
-
Vomiting
-
Diarrhea
-
Fever
-
Fatigue or weakness
Symptoms can begin within a few hours after eating contaminated food, but in some cases may appear days later depending on the cause.
Causes and Risk Factors
Food poisoning frequently results from:
-
Poor hand hygiene during food preparation
-
Unclean cooking utensils or surfaces
-
Foods left unrefrigerated for long periods
-
Improper reheating or storage temperatures
-
Undercooked eggs, meat, or seafood
-
Raw or unwashed fruits and vegetables
-
Cross-contamination between raw and cooked foods
Foods that contain mayonnaise or dairy products can spoil quickly if not kept chilled. Outdoor gatherings, buffets, and shared meals can increase exposure if food safety practices are overlooked.
First Aid Awareness and General Management
For mild food-related stomach upset:
-
Rest and avoid further questionable foods.
-
Drink small amounts of water or clear fluids regularly.
-
Monitor symptoms and energy levels.
Hydration is especially important because vomiting and diarrhea can quickly lead to fluid loss. If symptoms are severe, prolonged, or involve confusion, persistent vomiting, or signs of significant dehydration, professional assessment is generally recommended. First aid training focuses on recognizing when supportive care is enough and when additional help should be encouraged.
Prevention and Workplace Considerations
-
Wash hands thoroughly before handling food.
-
Keep hot foods hot and cold foods cold.
-
Refrigerate leftovers promptly.
-
Avoid cross-contamination between raw and cooked foods.
-
Label shared foods with preparation dates where possible.
-
Clean kitchen surfaces and utensils regularly.
-
Include food safety awareness in workplace health training.
Possible Complications to Be Aware Of
Most people recover within 24 hours to a few days. However, complications can occur, particularly with dehydration. Certain bacteria or parasites may lead to more serious effects in vulnerable populations such as older adults, young children, pregnant individuals, or those with weakened immune systems. Recognizing worsening symptoms early supports timely care.
Frequently Asked Questions
How quickly can food poisoning start?
Symptoms can appear within hours, but some types of contamination may take a day or more to show noticeable effects.
Is dehydration a concern?
Yes. Ongoing vomiting or diarrhea can lead to fluid loss, which is why steady hydration is an important first step in general management.
Can leftovers cause food poisoning?
Yes. Leftovers that are not refrigerated promptly or reheated thoroughly may allow bacteria to grow.
Does everyone who eats the same food get sick?
Not always. Individual immune responses, portion size, and existing health conditions can influence who develops symptoms.
Why is workplace food safety important?
Shared meals and kitchens increase exposure risk. Safe food handling and awareness reduce the chance of multiple people becoming unwell at the same time.
Educational Note
This content is for general public education and first aid awareness. Learning basic food safety and first aid skills can help individuals respond calmly and make informed decisions in everyday situations.