Nasal Congestion After Eating Chocolate: Allergy Awareness and First Aid Education
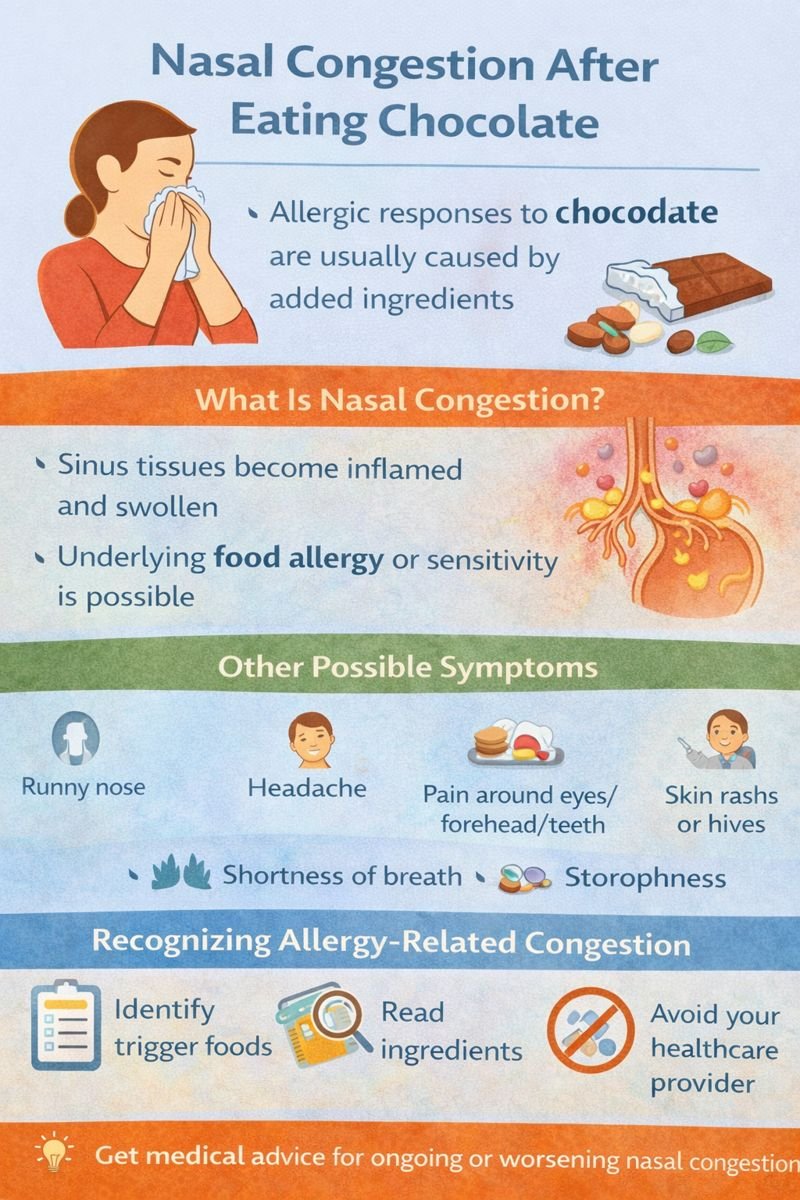
Developing nasal congestion after eating chocolate may seem unexpected, but for some individuals, it can be a sign of a food-related allergic response. Nasal congestion occurs when the tissues lining the sinuses become inflamed and swollen, restricting airflow through the nasal passages.
In people with food sensitivities or allergies, this reaction can happen shortly after consuming certain foods, including chocolate or ingredients commonly found in chocolate products.
First Aid & Workplace Relevance (Canada)
Food-related allergy symptoms, including nasal congestion, may affect individuals in Canadian workplaces such as offices, schools, childcare centres, healthcare settings, and food service environments. Congestion, headaches, or facial pressure can interfere with concentration, communication, and comfort during work tasks.
First aid awareness helps workers recognize when symptoms may be allergy-related rather than a cold or infection, supporting early assessment and safer food choices in shared environments.
Scenario: Recognizing a Food-Related Reaction
After eating a chocolate snack during a break, an employee noticed recurring nasal congestion and facial pressure that did not occur at other times. Remembering first aid training about food allergy awareness, they began checking ingredient labels more carefully and later discussed the pattern with a healthcare provider. Identifying a trigger helped prevent repeated discomfort at work.
What Is Found in Chocolate?
-
Ground cacao (cocoa) beans
-
Sugar
-
Cocoa butter
-
Flavouring ingredients
Many chocolate products also contain common food allergens, such as:
-
Tree nuts
-
Milk
-
Peanuts
-
Wheat
While an allergy to cacao itself is uncommon, reactions are more often linked to these added ingredients or cross-contamination during manufacturing.
What Is Nasal Congestion?
Nasal congestion is not a normal response to eating chocolate in otherwise healthy adults. When it occurs after eating, it may indicate an underlying sensitivity or allergy.
During an allergic response, the immune system releases chemicals such as histamine. Histamine increases blood flow and fluid leakage into tissues, causing swelling inside the sinuses. This swelling blocks normal airflow and leads to congestion.
Other Symptoms That May Occur
When nasal congestion is allergy-related, additional symptoms may include:
-
Runny nose
-
Postnasal drip
-
Facial tenderness or pressure
-
Headache
-
Pain around the eyes, cheeks, forehead, or upper teeth
Other food allergy symptoms may also appear, such as:
-
Skin rashes or hives
-
Itching
-
Coughing or wheezing
-
Shortness of breath
-
Chest tightness
-
Lightheadedness
Symptoms can vary in severity and may occur together.
First Aid Awareness and General Management
From a first aid education perspective, managing food-related nasal congestion focuses on recognition and avoidance, not treatment decisions.
Key awareness points include:
-
Identifying foods that consistently trigger symptoms
-
Reading ingredient and allergen labels carefully
-
Avoiding suspected trigger foods until assessed
-
Understanding that repeated exposure may worsen reactions
Medical assessment is needed to confirm food allergies and determine appropriate individual management strategies.
Prevention and Everyday Considerations
General preventive measures include:
-
Avoiding foods known to cause symptoms
-
Choosing chocolate products made without known allergens when appropriate
-
Being aware that ingredient lists and allergen warnings may change
-
Informing workplaces or schools of known food allergies when necessary
Canadian food labelling regulations require manufacturers to clearly identify priority allergens on packaged foods.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is nasal congestion after eating chocolate normal?
No. Nasal congestion after eating may suggest an underlying allergy or sensitivity rather than a normal response.
Is the allergy always caused by chocolate itself?
Often, reactions are linked to ingredients such as nuts or milk rather than cacao.
Can food allergies cause sinus pressure?
Yes. Allergic inflammation can cause swelling in the sinus tissues, leading to pressure and congestion.
Should mild symptoms still be checked?
Yes. Ongoing or recurring symptoms should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Can food allergy symptoms change over time?
Yes. Sensitivity levels and symptom patterns may change, making ongoing awareness important.
Educational Note
This article is intended for general public education and first aid awareness. It does not provide medical diagnosis or treatment advice. First aid training emphasizes recognizing allergic responses, avoiding triggers, and knowing when further assessment may be appropriate.
