Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fracture: Symptoms, Causes, and First Aid Awareness in Canada
What Is a Calcaneus Fracture?
A calcaneus fracture is a break in the heel bone, one of the largest and most important bones in the foot. The calcaneus forms the foundation of the heel and plays a key role in walking, balance, and weight-bearing. Because of its role and position, a fracture to this bone is often considered debilitating, especially when caused by high-impact forces.
Calcaneus fractures frequently affect the subtalar joint, which allows the foot to move on uneven or sloped surfaces. Damage to this joint can result in stiffness and long-term walking difficulties.
First Aid and Workplace Relevance in Canada
Heel bone fractures are most often seen in Canadian workplaces and activities involving heights, ladders, scaffolding, construction, roofing, and motor vehicle travel. Slips, falls, and collisions are common mechanisms of injury.
First aid awareness of fractures helps workers recognize serious foot injuries early, avoid weight-bearing when appropriate, and seek timely medical assessment—reducing the risk of complications and prolonged disability.
A Simple, Realistic Scenario
A construction worker falls from a low scaffold and lands hard on their feet. Although they can stand briefly, heel pain and swelling increase quickly. Remembering first aid training, they avoid putting weight on the foot, keep it supported, and arrange immediate medical evaluation.
Common Causes of Calcaneus Fractures
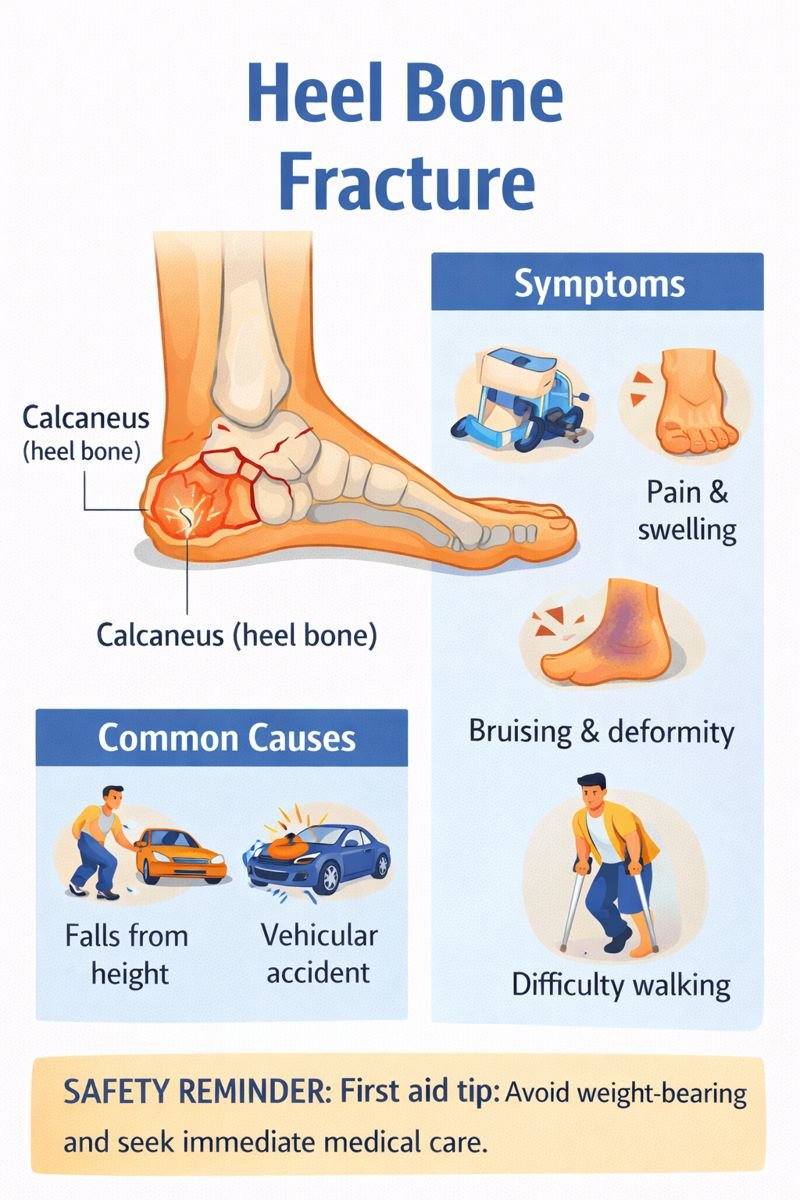
-
Falls from height landing on the feet
-
Motor vehicle or motorcycle collisions
-
Heavy impacts or crushing injuries
-
Severe twisting forces to the foot
When a person lands on their feet after a fall, body weight drives the talus bone downward into the calcaneus, causing it to crack or shatter. Different injury mechanisms can produce similar fracture patterns.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
Symptoms of a calcaneus fracture may include:
-
Heel pain
-
Swelling of the foot or ankle
-
Bruising around the heel or sole
-
Visible heel deformity
-
Difficulty or inability to bear weight
In less severe cases, pain may allow limited walking with a limp. However, changes in heel shape can affect how the Achilles tendon transfers force, leading to instability and altered walking patterns.
First Aid and Early Management
From a first aid perspective, suspected heel fractures should be treated as serious injuries.
General first aid considerations include:
-
Avoiding weight-bearing on the affected foot
-
Supporting and immobilizing the foot and ankle
-
Elevating the foot if possible
-
Seeking medical assessment promptly
Early care focuses on preventing further damage and managing swelling until proper diagnosis is made.
Diagnosing a Calcaneus Fracture
Medical assessment includes discussing how the injury occurred and evaluating the foot for circulation, nerve function, and alignment. Imaging such as X-rays and CT scans is commonly used to confirm the fracture and assess joint involvement.
Calcaneus fractures often occur alongside other injuries, especially after high-impact events, making thorough assessment important.
Treatment and Recovery Considerations
Treatment decisions depend on:
-
Overall health of the individual
-
Severity and pattern of the fracture
-
Soft tissue involvement
-
Whether the bone fragments are displaced
The main goal of treatment is to restore the normal shape and alignment of the heel, as better anatomical restoration is linked to improved outcomes.
Non-Surgical Management
If the bone fragments remain well aligned, treatment may involve:
-
Immobilization with a cast or boot
-
Strict avoidance of weight-bearing
-
Gradual healing over 6 to 8 weeks or longer
Surgical Management
If the fracture is displaced or the heel structure is significantly altered, surgery may be considered to realign the bone. Surgical treatment carries higher risks and is carefully evaluated on an individual basis.
Prevention and Workplace Safety Tips
Reducing the risk of heel fractures involves fall and impact prevention.
Helpful measures include:
-
Using fall protection and guardrails when working at heights
-
Wearing appropriate footwear
-
Keeping work areas clear of trip hazards
-
Following vehicle safety practices
-
Reporting unsafe conditions promptly
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are calcaneus fractures considered serious?
They often involve joints and weight-bearing surfaces, which can affect long-term mobility.
Can someone walk with a heel fracture?
Some minor fractures allow limited walking, but weight-bearing can worsen the injury.
Why does walking feel unstable after this injury?
Damage to the heel affects how muscles and tendons transfer force during walking.
Do calcaneus fractures often involve other injuries?
Yes. They frequently occur during high-impact events that affect multiple body parts.
How does first aid training help with foot injuries?
First aid training emphasizes immobilization, avoiding weight-bearing, and early medical care.
Educational Note
This article is intended for general public education and workplace first aid awareness in Canada. It does not replace medical assessment, diagnosis, or individualized treatment for foot injuries.
