Foot Rashes: First Aid Awareness and Skin Care in Canada
What Are Foot Rashes?
Foot rashes refer to redness, bumps, scaling, or irritation on the skin of the feet. They can appear on the heels, toes, soles, or the top of the foot. Some rashes are short-term and mild, while others can persist and require closer attention. Public education focuses on recognizing common patterns, supporting gentle skin care, and reducing spread, rather than diagnosing specific conditions.
Why Foot Rash Awareness Matters in Canadian Homes and Workplaces
In Canada, footwear choices, seasonal moisture, shared change rooms, and long work shifts in boots or safety shoes can all affect foot skin. First aid awareness helps people notice early irritation, keep feet clean and dry, and avoid sharing personal items—especially in gyms, schools, industrial sites, and healthcare settings.
A Simple, Realistic Scenario
After several long shifts in steel-toe boots, a worker notices itchy, red patches between the toes. Remembering basic skin-hygiene awareness, they start drying their feet thoroughly after showers, rotate breathable socks, and avoid tight footwear on days off. The irritation gradually improves.
Common Signs and Symptoms
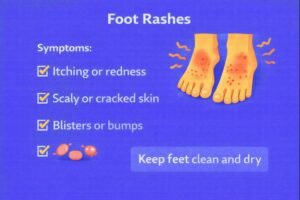
-
Red or pink patches of skin
-
Itchiness or burning sensation
-
Flaky, scaly, or peeling areas
-
Small blisters or bumps
-
Cracking around toes or heels
-
Temporary discomfort when walking
Symptoms may be mild at first and become more noticeable with moisture, friction, or scratching.
Possible Contributing Factors
Allergic or Irritant Reactions
-
Sensitivity to shoe materials, dyes, soaps, or creams
-
Contact with plants or cleaning products
-
Rash edges may look well-defined or appear where footwear touches the skin
Chronic or Recurrent Skin Conditions
-
Ongoing dryness, scaling, or thickened patches
-
Flare-ups can be linked to stress, weather, or skin injury
Fungal Irritation (Often Called “Athlete’s Foot”)
-
Common in warm, damp areas such as between the toes
-
Can spread in shared showers or locker rooms
-
Presents with itching, peeling, or ring-shaped patches
Contagious Skin Irritation
-
Some itchy rashes can spread through close contact or shared bedding/clothing
-
May appear as small bumps with intense itching
First Aid Awareness and General Comfort Measures
From a public-education perspective, the emphasis is on cleanliness, dryness, and gentle care:
-
Wash feet daily with mild soap and rinse thoroughly
-
Dry carefully between toes after bathing or swimming
-
Change socks regularly and choose breathable fabrics
-
Avoid scratching to reduce further irritation
-
Use clean towels and avoid sharing footwear or nail tools
-
Monitor for spreading redness, swelling, or drainage and seek further guidance if concerns arise
These steps support comfort and help limit ongoing irritation.
Prevention and Everyday Considerations in Canada
-
Rotate shoes to allow them to dry fully between uses
-
Wear flip-flops or sandals in public showers and locker rooms
-
Keep nails trimmed and feet moisturized (but avoid excess moisture between toes)
-
Choose well-fitting footwear with ventilation, especially for long work shifts
-
Launder socks and towels in warm water and dry completely
Such habits help maintain healthy foot skin at home, school, sports facilities, and workplaces.
Frequently Asked Questions About Foot Rashes
Are all foot rashes contagious?
No. Some are related to irritation or allergies, while others can spread through close contact or shared items.
Why do rashes often appear between the toes?
Moisture and warmth can build up in these areas, increasing skin sensitivity.
Can footwear make a difference?
Yes. Tight or non-breathable shoes can trap sweat and increase friction.
Does scratching make rashes worse?
Scratching can damage the skin surface and increase redness or crusting.
When should a rash be checked further?
If it persists, spreads quickly, becomes very painful, or shows swelling or drainage, further assessment is advisable.
Educational Note
This article is intended for general public and workplace education in Canada. It supports awareness of foot skin irritation and first aid recognition but does not replace evaluation or care from qualified healthcare professionals.
