Tibial Plafond Fractures: First Aid Awareness, Ankle Injuries, and Workplace Safety in Canada
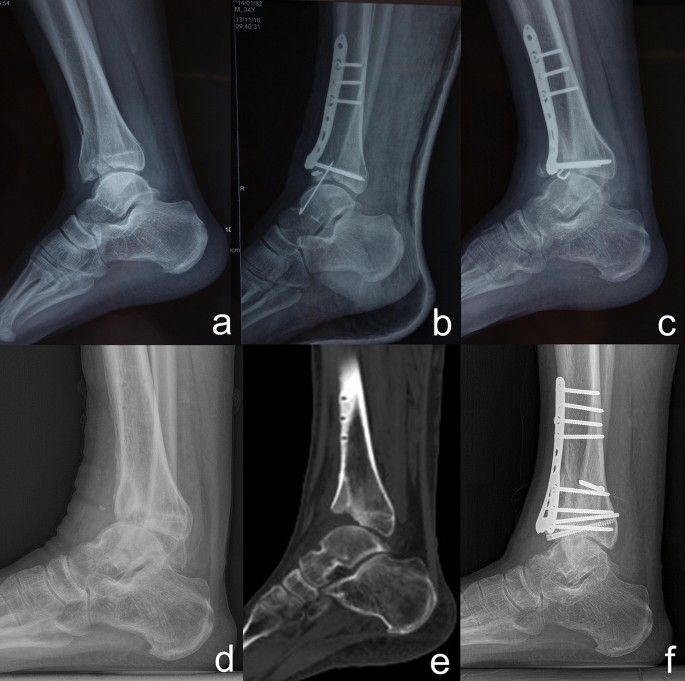
From a first aid and workplace safety perspective, tibial plafond fractures are critical injuries. They often result from high-energy trauma, require careful immobilization, and carry a significant risk of chronic pain, stiffness, and early-onset ankle arthritis—even with proper treatment.
This article is provided for education and safety awareness only and does not replace medical advice or diagnosis.
Why Tibial Plafond Fractures Matter for First Aid and Safety
In Canadian workplaces and public settings, tibial plafond fractures are especially concerning because they:
-
Involve the ankle joint surface directly
-
Severely limit weight-bearing and walking
-
Are often associated with major swelling and soft tissue damage
-
Can result in prolonged recovery and long-term disability
First aiders should recognize that ankle injuries with severe pain, swelling, or deformity are never minor.
Understanding the Injury
Tibial plafond fractures occur:
-
Just above the ankle joint
-
Through the cartilage surface that allows smooth ankle movement
These fractures are similar in concept to joint-surface fractures elsewhere in the body. Preserving joint alignment and protecting cartilage are key goals of treatment, but even optimal care cannot always prevent future joint problems.
The Role of Soft Tissue Injury
One of the most important challenges with tibial plafond fractures is the condition of the soft tissues around the ankle.
The ankle has:
-
Very little muscle coverage
-
Thin skin
-
Limited space for swelling
As a result:
-
Swelling can become severe
-
Surgical incisions may not be safe initially
-
Definitive surgery is often delayed until swelling subsides
During this waiting period, the fracture must still be stabilized to prevent further damage.
First Aid Response: Immediate Priorities
From a first aid perspective:
-
Do not allow weight-bearing
-
Immobilize the ankle and lower leg using a splint if trained to do so
-
Elevate the limb to reduce swelling
-
Apply cold packs around (not directly on) the injury
-
Treat the injury as urgent and arrange medical transport
Visible deformity, open wounds, or extreme pain indicate a medical emergency.
Temporary Stabilization Methods
While soft tissues heal, stabilization may include:
-
Splints or casts
-
External fixation devices applied surgically
An external fixator holds the bones steady above and below the fracture while avoiding damaged skin and soft tissue. This allows swelling to decrease while maintaining alignment and monitoring healing.
Treatment Options After Swelling Improves
Once soft tissues are ready, several treatment approaches may be used depending on fracture severity.
Casting
Used when fracture fragments are minimally displaced or when surgery is not safe. Casting may also be chosen when soft tissue damage is extensive.
External Fixation
May be used temporarily or as definitive treatment in cases with:
-
Severe swelling
-
Open fractures
-
Significant soft tissue injury
Limited Internal Fixation
Uses small incisions to secure key fracture fragments. This method reduces soft tissue disruption and is often combined with casting or external fixation.
Internal Fixation
Plates and screws are used to restore bone alignment more precisely. Even with excellent alignment, ankle arthritis remains a common long-term complication.
Ankle Fusion (Severe Cases)
In cases where joint restoration is unlikely:
-
Ankle fusion may be considered
-
Fusion eliminates motion but provides a stable, less painful platform for walking
This option is typically reserved for severe or irreparable injuries.
Long-Term Risks and Recovery
People with tibial plafond fractures face:
-
Long recovery periods
-
Extended non–weight-bearing phases
-
Reduced ankle mobility
-
High risk of early ankle arthritis
Return to physically demanding work may take months and may require accommodations.
Workplace and Safety Considerations
These fractures can significantly affect:
-
Ability to stand, walk, or climb safely
-
Return-to-work timelines
-
Long-term job suitability in physical roles
Early recognition, proper first aid response, and realistic recovery planning are essential for safety and rehabilitation.
Key Takeaways for Canadians
-
Tibial plafond fractures are serious ankle joint injuries
-
Swelling and soft tissue damage complicate treatment
-
First aid focuses on immobilization and rapid medical care
-
Long-term ankle issues are common even with proper treatment
Educational Disclaimer
This article is provided for general education and first aid awareness only. It does not diagnose or treat fractures. Anyone with a suspected ankle fracture should seek immediate professional medical care.
