MRSA and Pneumonia: Symptoms and What to Watch For
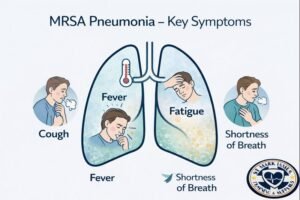
Respiratory Symptoms
Cough and Phlegm Changes
Pneumonia often causes cough, which may produce mucus (phlegm). Changes in mucus colour can occur during respiratory infections, but colour alone does not confirm severity. Healthcare providers assess symptoms as a whole, including breathing, fever, and duration.
Shortness of Breath & Wheezing
Breathing may feel more difficult due to inflammation in the lungs. Wheezing or breathlessness during regular breathing or activity can also develop.
Systemic Symptoms (Body-Wide Reactions)
Fever & Chills
Fever is common as the immune system responds to infection. Chills or sweats may accompany temperature changes. Older adults or individuals with weakened immune systems may show lower or atypical temperatures.
Fatigue & Weakness
Feeling drained, tired, or unwell is common with pneumonia, especially when layered on top of prior flu symptoms.
Muscle & Head Aches
Aches, headache, and general malaise may appear early and overlap with typical viral symptoms.
Chest Discomfort
Discomfort or soreness in the chest can occur due to coughing or inflammation in the tissues surrounding the lungs. Persistent coughing can make the chest muscles feel tired or sore.
Digestive Symptoms
Some people experience nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea alongside respiratory symptoms — particularly when the body is responding to infection or medications.
Flu vs. Pneumonia Progression
Many cases of bacterial pneumonia occur after an initial viral illness. A pattern sometimes seen is:
-
Flu-like symptoms first (fever, aches, fatigue)
-
Respiratory symptoms intensify (persistent cough, shortness of breath)
Any combination that worsens instead of improving may prompt medical evaluation.
Healthcare & Canadian Context
MRSA matters most in:
-
Hospitals and long-term care homes
-
Community health and shelter settings
-
Correctional facilities
-
Households with close contact
-
Individuals recovering from influenza
-
People with weakened immune systems
In Canada, infection control measures, mask fit testing, hand hygiene programs, and first aid/CPR training all contribute to safer workplaces and better early recognition of symptoms.
Disclaimer
This post is for public education only and not a substitute for medical assessment. Canadians with worsening respiratory symptoms, persistent fever, or difficulty breathing should seek guidance from a qualified healthcare professional.
