Greenstick Fractures in Children: Causes, Symptoms & First Aid Guidance (Canada)
Educational Note: This post is for learning purposes only and does not replace medical assessment or first aid training. In Canada, proper first aid knowledge — including how to recognize fractures — is commonly taught through accredited first aid and workplace safety courses.
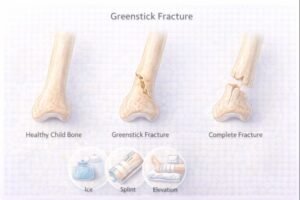
Why Greenstick Fractures Occur
Children’s bones are:
-
more porous
-
more elastic
-
still growing
This makes fractures present differently than in adults. Because of this, pediatric fractures often require different evaluation and management considerations.
How to Recognize a Greenstick Fracture
The signs may be subtle. A child may:
-
guard or avoid using the limb
-
wince or cry when touched
-
show swelling or mild deformity
-
complain of pain during movement
Unlike a complete fracture, the limb may look mostly normal in shape.
Diagnosis
A healthcare provider typically orders:
-
X-rays (often both sides for comparison)
-
CT scans in selected cases
This ensures the injury is properly classified and that no additional structures are affected.
Treatment & Recovery
The most common treatment is splinting, which immobilizes the limb while allowing for swelling. Splints may be:
-
plaster or fiberglass (custom-formed)
-
secured using elastic bandages
After initial care, children often:
-
keep the limb elevated
-
apply ice intermittently
-
use prescribed medications for pain & swelling
Healing time ranges from weeks to a few months, but pediatric bone healing tends to be faster than adults. Follow-up imaging is common to ensure proper alignment during growth.
Canadian First Aid Context
Although greenstick fractures are medical injuries, early first aid response plays an important role — especially in:
-
schools
-
sports programs
-
childcare environments
-
workplaces employing young workers (e.g., summer camps, recreation)
Canadian first aid and injury prevention training emphasizes:
-
safe immobilization
-
minimizing movement
-
preventing additional damage
-
knowing when to seek emergency care
Disclaimer
This article is for public education only and should not be used for diagnosis or treatment decisions. For concerns about fractures or injuries, seek medical care. Training through recognized first aid and workplace safety courses can improve preparedness for real-life emergencies.
