Knee Joint Infection (Septic Arthritis): Symptoms, Causes, and First Aid Awareness in Canada
What Is a Knee Joint Infection?
The knee joint is a complex structure made up of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and other tissues that work together to allow smooth movement. The joint is lubricated by synovial fluid, which reduces friction during motion. When this fluid becomes infected by bacteria, the condition is known as septic arthritis.
The knee is one of the most common joints affected by septic arthritis. This condition can develop quickly and may cause serious joint damage if not identified and managed early.
First Aid and Workplace Relevance in Canada
Knee joint infections are relevant in Canadian workplaces and community settings, particularly where individuals experience knee injuries, puncture wounds, or underlying health conditions. Workers who kneel frequently, sustain cuts near the knee, or have chronic health issues may be at higher risk.
First aid awareness helps individuals recognize early warning signs of serious joint conditions and understand when urgent medical assessment is needed to prevent long-term complications.
A Simple, Realistic Scenario
A warehouse worker notices sudden knee swelling, warmth, and increasing pain over a short period, along with feeling unwell. Remembering first aid education, they avoid putting weight on the knee and seek immediate medical assessment. Early care helps limit joint damage.
Common Symptoms of Knee Joint Infection
Septic arthritis often causes rapid and severe symptoms, which may include:
-
Intense knee pain
-
Swelling and joint stiffness
-
Redness and warmth over the knee
-
Reduced ability to move the joint
-
Fever or feeling unwell
Fluid buildup inside the knee, sometimes referred to as “water on the knee,” may occur early. In children, symptoms can include irritability, reduced appetite, and reluctance to move the leg.
Possible Causes and Risk Factors
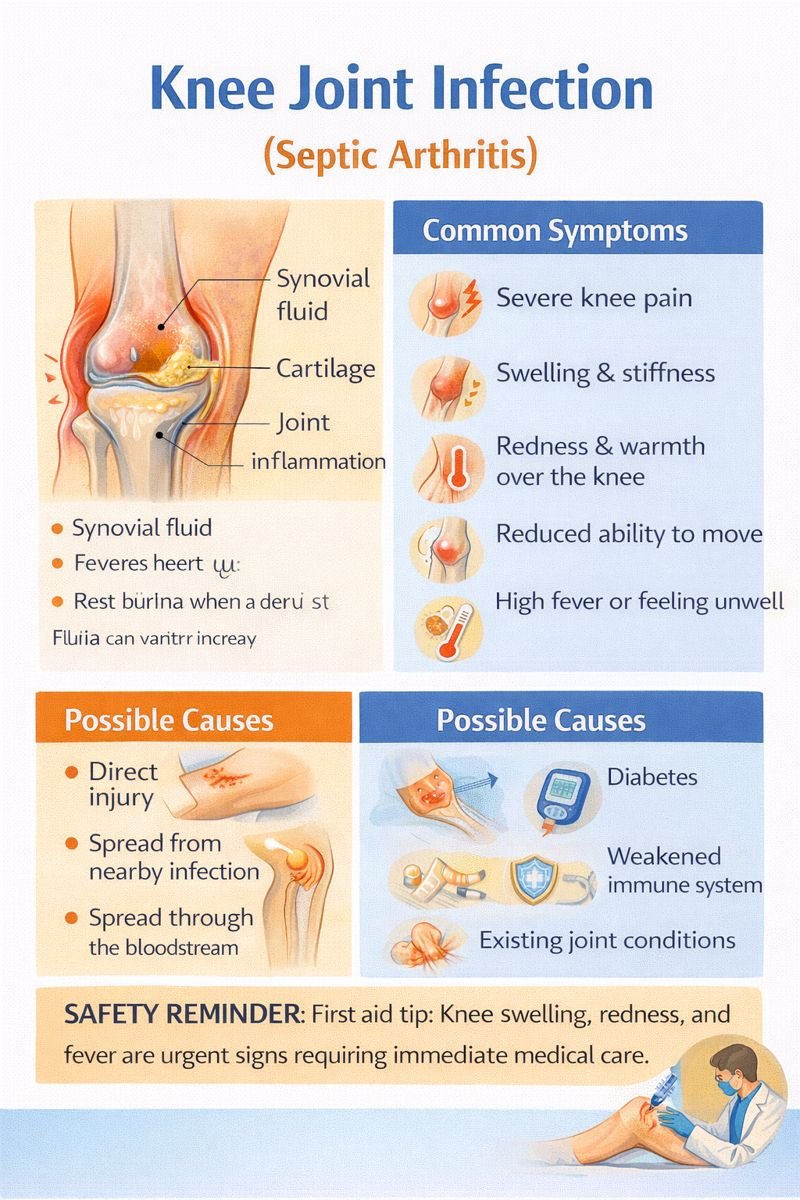
-
Spread from a nearby skin or soft tissue infection
-
Spread through the bloodstream from another infection
Certain conditions increase the risk of knee joint infection, such as:
-
Diabetes
-
Conditions that weaken the immune system
-
Existing joint conditions, including inflammatory arthritis
First Aid Awareness and Early Response
From a first aid perspective, suspected knee joint infection should be treated as a medical urgency.
General first aid considerations include:
-
Limiting movement of the affected knee
-
Avoiding weight-bearing if painful
-
Monitoring for fever or worsening symptoms
-
Seeking immediate medical evaluation
Early action is critical to protect the joint and reduce the risk of lasting damage.
Diagnosing Knee Joint Infection
Diagnosis focuses on evaluating the synovial fluid within the knee. Healthcare providers may:
-
Remove joint fluid using a needle to check for infection
-
Test the fluid for bacteria and signs of inflammation
-
Use imaging to assess joint and bone involvement
-
Perform blood tests to detect infection in the bloodstream
These steps help confirm the diagnosis and guide treatment decisions.
Treatment and Management Considerations
Management of knee joint infection typically involves:
-
Draining infected fluid from the joint to relieve pressure
-
Using antibiotics to control the infection
-
Ongoing monitoring to ensure the infection clears
Treatment often begins in a hospital setting and may be adjusted as more information becomes available about the infection.
Importance of Early Identification
Prompt recognition and treatment of septic arthritis are essential. Without proper care, the infection can lead to:
-
Chronic joint inflammation
-
Permanent joint damage
-
Knee deformity
-
Difficulty walking and reduced mobility
Early awareness and medical intervention greatly improve outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is septic arthritis considered serious?
It can quickly damage joint structures if not treated early.
Can knee joint infection develop without an obvious injury?
Yes. Infections can spread through the bloodstream or from nearby tissues.
Is swelling always present with knee joint infection?
Swelling is common and often one of the earliest signs.
Are children affected by knee joint infections?
Yes. Children may show different signs, such as irritability and reduced movement.
How does first aid training help with joint infections?
First aid education promotes early recognition and rapid medical referral.
Educational Note
This article is intended for general public education and workplace first aid awareness in Canada. It does not replace medical assessment, diagnosis, or treatment for joint infections.
