Tuberculosis (TB): Latent vs. Active and Common Symptoms
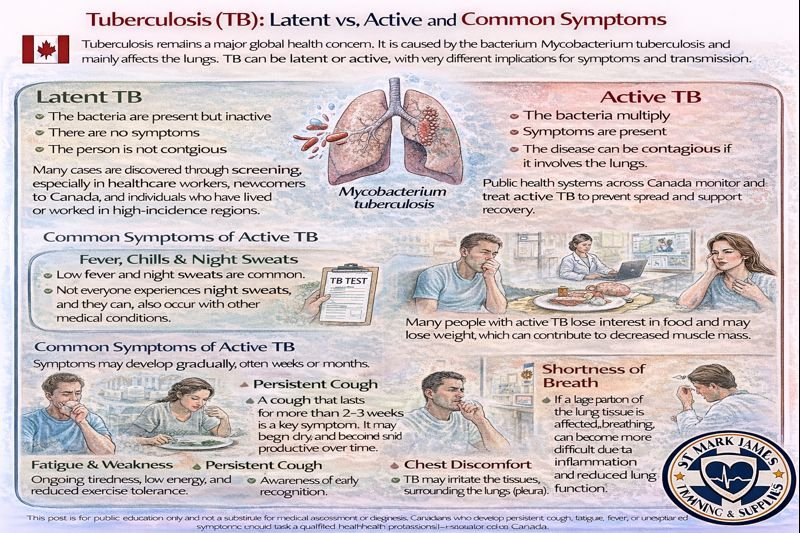
Latent TB
In latent TB:
-
The bacteria are present but inactive
-
There are no symptoms
-
The person is not contagious
Many cases are discovered through screening, especially in healthcare workers, newcomers to Canada, and individuals who have lived or worked in high-incidence regions.
Active TB
In active TB:
-
The bacteria multiply
-
Symptoms are present
-
The disease can be contagious if it involves the lungs
Public health systems across Canada monitor and treat active TB to prevent spread and support recovery.
Common Symptoms of Active TB
Symptoms may develop gradually, often over weeks or months.
Fever, Chills & Night Sweats
Low fever and night sweats are common. Not everyone experiences night sweats, and they can also occur with other medical conditions.
Appetite Loss & Unintentional Weight Loss
Many people with active TB lose interest in food and may lose weight, which can contribute to decreased muscle mass in prolonged cases.
Fatigue & Weakness
Ongoing tiredness, low energy, and reduced exercise tolerance are frequently reported.
Persistent Cough
A cough that lasts for more than 2–3 weeks is a key symptom. It may begin dry and become more productive over time. In some cases, mucus may contain small streaks of blood, although this varies.
Shortness of Breath
If a large portion of the lung tissue is affected, breathing can become more difficult due to inflammation and reduced lung function.
Chest Discomfort
TB may irritate the tissues surrounding the lungs (pleura), which can make deep breathing or coughing uncomfortable.
Voice Changes or Throat Irritation
If the upper airway becomes involved, hoarseness or difficulty swallowing may develop.
Public Health & Canadian Context
Canada has strong TB control programs, but cases still occur, especially in:
-
Newcomers from higher-incidence regions
-
Remote areas with limited healthcare access
-
Healthcare and long-term care settings
-
Individuals with weakened immune systems
-
People traveling for work or humanitarian missions
Awareness and early recognition are essential for preventing spread and ensuring successful treatment.
Workplace & Safety Training Relevance
TB intersects with occupational safety in:
-
Healthcare
-
Long-term care and community health
-
Correctional facilities
-
Shelters and outreach programs
-
Immigration services and travel health
This aligns with broader Canadian training programs that emphasize prevention, assessment skills, and emergency preparedness — including first aid, CPR/AED, workplace safety education, and mask fit testing.
Disclaimer
This post is for public education only and not a substitute for medical assessment or diagnosis. Canadians who develop persistent cough, fatigue, fever, or unexplained symptoms should consult a qualified healthcare professional.
