Avulsion Fractures: What They Are and How They’re Managed (Canada-Focused Educational Overview)
Educational note: This article is for general learning only and does not replace professional medical assessment or first aid. A healthcare provider should evaluate any suspected fracture.
Common Causes & Who is Most Affected
✔ Sudden muscular contractions (e.g., jumping, sprinting, quick direction changes)
✔ Falls or collisions during sports and play
✔ Workplace strain or unexpected lifting/twisting
✔ Growth plates in children make bone more vulnerable than tendons
Avulsion fractures are often straightforward and heal well, especially when recognized and managed early.
Signs to Watch For
Symptoms may include:
-
Sudden localized pain
-
Swelling or bruising
-
Trouble bearing weight or moving the area
-
Tenderness at the tendon/ligament attachment site
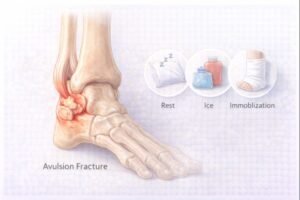
How Avulsion Fractures Are Managed
1. Rest & Ice
The first line of care typically involves rest from physical activity and application of ice to reduce swelling or discomfort.
From a first aid standpoint, a RICE-based approach (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) may be used if appropriate.
2. Immobilization
If symptoms are moderate or if the bone fragment is displaced, a healthcare provider may immobilize the area using a cast or brace for 4–6 weeks.
Follow-up X-ray imaging helps determine whether healing is progressing well.
3. Surgical Repair (In More Severe Cases)
Surgery may be required when:
-
A tendon or ligament is severely torn
-
The bone fragment is unstable
-
Function would be impaired without repair
Surgical repair may involve pins, screws, or other stabilizing hardware. Rehabilitation and strengthening typically follow.
Recovery & Returning to Activity
Most avulsion fractures heal successfully with proper management.
Children and youth usually recover well, although clearance from a healthcare provider is recommended before returning to sports or strenuous activity.
Why This Matters for Canadian Workplaces & Training
While many avulsion fractures occur in sports or recreation, similar mechanisms can occur in workplaces, especially in roles involving:
-
sudden manual handling
-
slips and falls
-
rapid movement or force
This is one reason Canadian employers continue investing in occupational health and safety education, early injury recognition, and proper first aid skills.
St. Mark James Training offers first aid, CPR/AED, and workplace safety certification across Canada, helping individuals and employers learn how to respond confidently to injuries — including musculoskeletal issues like suspected fractures — until medical care is available.
Disclaimer:
This content is for general education only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or emergency care. Always seek assessment from a qualified healthcare provider for suspected fractures or injuries.
