Lower Back Spasms: Causes, Symptoms, and First Aid Awareness in the Canadian Workplace
What Are Back Spasms?
A back spasm is an involuntary tightening or contraction of muscles in the lower back. Many people in Canada experience back pain at some point in their lives, and muscle spasms are a common cause. Back spasms can range from mild stiffness and discomfort to more intense pain that makes movement difficult.
In many cases, back spasms are related to muscle strain and can be managed without surgery. Occasionally, they may be associated with underlying spinal or nerve-related conditions, which require further medical assessment.
First Aid and Workplace Relevance in Canada
Back spasms are especially relevant in Canadian workplaces that involve lifting, repetitive movements, prolonged sitting, or physical labour. They are a common reason for missed workdays and modified duties.
First aid awareness helps workers recognize early signs of muscle strain, respond appropriately, and reduce the risk of further injury. Knowing when to rest, apply basic care measures, and seek medical evaluation supports safer workplaces and quicker recovery.
A Simple, Realistic Scenario
A warehouse employee feels sudden tightness in their lower back after lifting several boxes during a shift. Remembering their workplace safety training, they stop the task, report the discomfort to their supervisor, and use basic first aid measures such as rest and temperature therapy. Modified duties are arranged while the muscles recover.
Symptoms of Lower Back Spasms
Back spasms may present with:
-
Sudden tightening or cramping in the lower back
-
Stiffness or reduced range of motion
-
Muscle tenderness
The intensity can vary, and symptoms may improve with rest or persist if the muscles remain strained.
Causes and How Back Spasms Develop
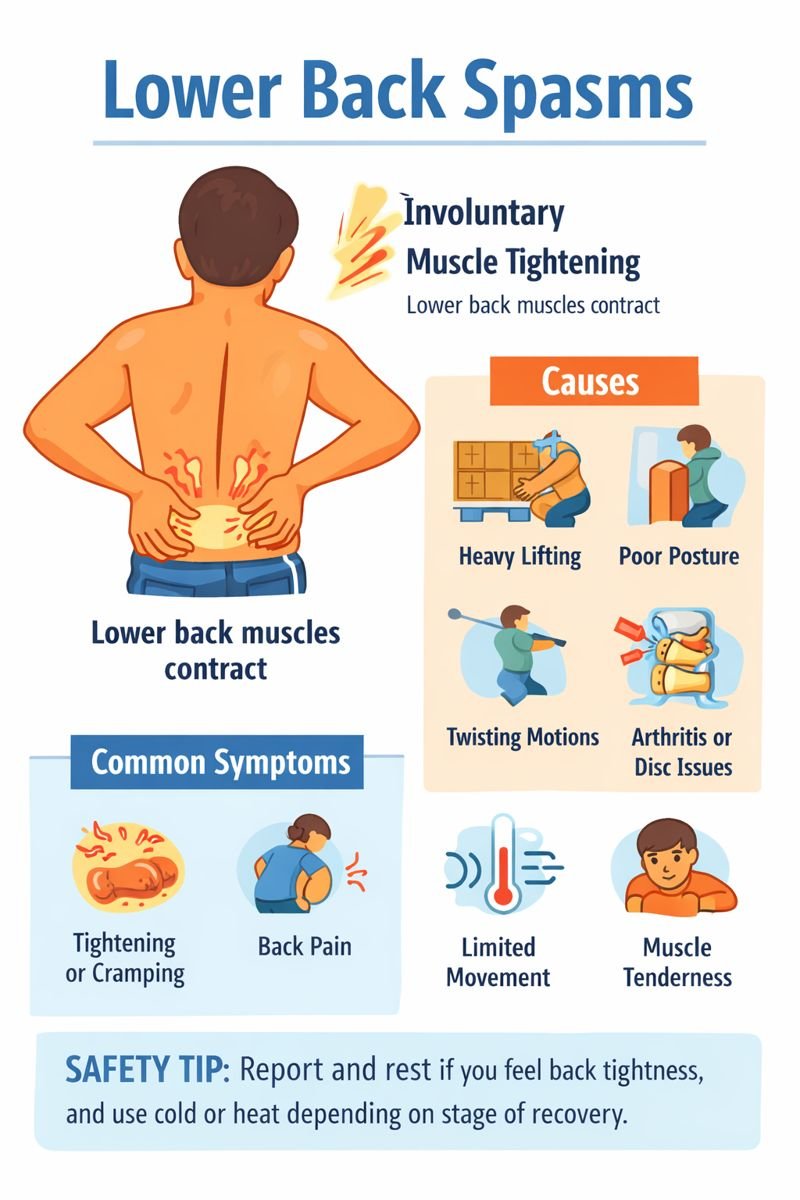
Common causes include:
-
Lifting heavy or awkward objects
-
Sudden or repetitive twisting motions
-
Poor posture or prolonged sitting
-
Weak abdominal (core) muscles that reduce spinal support
-
Sports involving rapid or repeated back rotation, such as golf or football
Back spasms may also be associated with underlying conditions such as arthritis or spinal disc issues. These conditions can place pressure on nerves or the spinal cord, contributing to pain and muscle tightening.
First Aid and General Management
When back spasms follow physical strain or overuse, basic first aid measures may help support recovery.
General approaches often include:
-
Resting from activities that strain the back
-
Using cold applications early to help reduce inflammation
-
Using gentle heat later to support muscle relaxation and blood flow
In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend medications or other treatments as part of medical management. From a first aid and workplace perspective, the focus is on comfort, protection of the area, and preventing further strain.
Prevention and Workplace Considerations
Because the back is used constantly throughout the day, prevention plays an important role.
Helpful strategies include:
-
Using proper lifting techniques and mechanical aids when available
-
Maintaining good posture when standing or sitting
-
Keeping muscles flexible and strong through regular physical activity
-
Strengthening the core muscles that support the spine
-
Wearing stable, supportive footwear
-
Reducing unnecessary strain through ergonomic workplace design
Early reporting of back discomfort and adjusting tasks can help prevent minor muscle issues from becoming more serious injuries.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are back spasms the same as general back pain?
Back spasms involve muscle tightening, while back pain can have many causes, including joints, discs, or nerves.
Can back spasms happen without a specific injury?
Yes. Poor posture, muscle fatigue, or repetitive movements can lead to spasms even without a clear injury event.
Why are core muscles important for back health?
Abdominal and core muscles help support the spine and reduce strain on the lower back during movement.
Do back spasms always mean something serious?
Not always. Many spasms are related to muscle strain, but ongoing or worsening symptoms should be medically assessed.
How does first aid training help with back injuries?
First aid training emphasizes early recognition, safe response, activity modification, and prevention strategies for musculoskeletal injuries.
Educational Note
This article is intended for general education and workplace first aid awareness in Canada. It does not replace medical assessment or individualized care for back pain or injury.
