Understanding the Rule of Nines for Burns: First Aid Awareness and Severity
Workplace and first aid relevance (Canada)
Burns can occur in workplaces that involve hot equipment, steam, chemicals, or outdoor sun exposure. Awareness of how severity is estimated can support first aid responders and safety personnel in recognizing when burns may be serious and ensuring quick access to emergency help without attempting advanced care on site.
Scenario story
During a catering event, hot water splashed onto Liam’s forearm. The skin became red and painful. His supervisor ran cool tap water over the area and kept the arm elevated. Because the burn was small and superficial, the discomfort eased over time, and Liam later reviewed workplace safety procedures to avoid future incidents.
What affects burn severity?
Several factors are considered when estimating severity, including:
-
Depth of the burn (superficial, partial-thickness, or deeper injuries)
-
Surface area involved
-
Location of the burn
-
Cause of the burn
Since people vary in size and shape, the Rule of Nines uses proportional sections of the body rather than exact measurements.
Common causes of burns
Burns may result from:
-
Heat or open flames
-
Hot liquids and steam
-
Sun exposure or other ultraviolet (UV) radiation
-
Contact with chemicals
-
Electrical energy
-
Radiant heat sources
Superficial burns often heal without special care, while deeper or extensive burns may require urgent assessment to prevent complications.
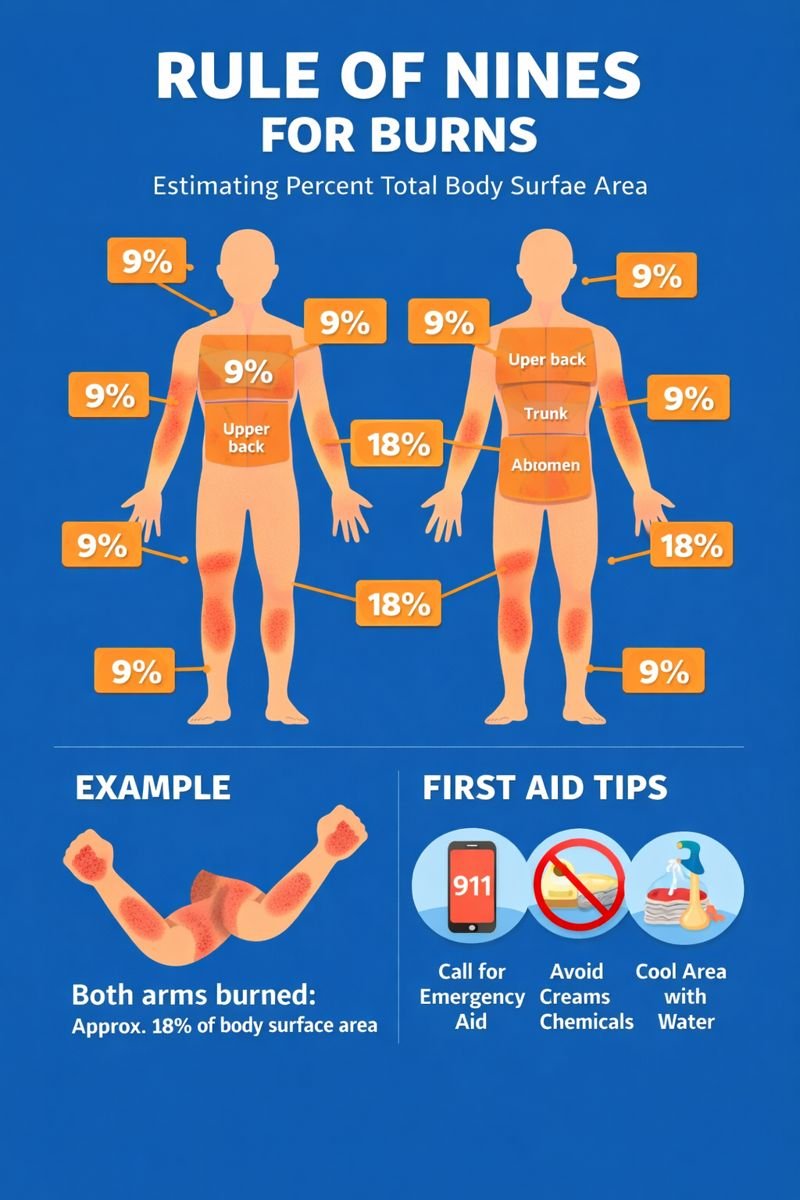
What is the Rule of Nines?
The Rule of Nines divides the body into sections, each representing approximately 9% (or multiples of 9%) of the body’s surface area. These include:
-
Head
-
Left arm
-
Right arm
-
Trunk
-
Abdomen
-
Upper back
-
Lower back
-
Left thigh
-
Right thigh
-
Left leg
-
Right leg
These areas combined represent roughly 99% of the body’s surface area, with the remaining percentage attributed to the genital region.
How the Rule of Nines is used
When estimating burn size:
-
Add the percentages of the areas affected by partial-thickness (second-degree) or deeper burns.
-
For example, a burn affecting both arms would represent about 18% TBSA.
-
If only part of an area is affected (e.g., half the chest), it may be estimated as 4.5% TBSA.
The Rule of Nines is primarily used in the field by trained responders to help determine whether special emergency care may be required. Hospitals have more advanced tools for precise assessment.
Complications and critical burns
Burns affecting large areas can increase the risk of complications, including:
-
Infection
-
Fluid loss and dehydration
-
Temperature regulation issues, such as hypothermia
Burns affecting more than 10% TBSA are generally considered significant and require emergency attention.
First aid and management awareness
When someone has a serious burn:
-
Seek emergency assistance promptly
-
Avoid breaking blisters or applying creams or chemicals
-
Keep the environment safe and avoid further exposure to heat or chemicals
-
Support airway, breathing, and circulation if needed, without providing advanced interventions
First aid responders should focus on safety and rapid activation of emergency services rather than attempting specialized medical care.
Prevention and workplace considerations
-
Use protective gloves, aprons, and eyewear when working with hot liquids or equipment
-
Follow safe handling procedures for chemicals
-
Implement sun safety practices for outdoor work
-
Maintain clear emergency response plans and first aid training in the workplace
FAQ
What makes a burn “critical”?
A burn may be considered critical if it is deep, covers a large area, affects sensitive regions (such as hands, face, feet, or groin), or is caused by chemicals, electricity, or open flames.
Do all burns need emergency care?
Superficial burns often heal without special treatment. Larger or deeper burns, especially those involving more than 10% TBSA, are more likely to require emergency attention.
Why is the Rule of Nines still used?
It provides a fast and reasonably accurate field estimate of burn size, helping responders determine urgency and appropriate care pathways.
Can children use the Rule of Nines?
Children have different body proportions, so modified tools are used in paediatric settings to estimate surface area more accurately.
Does burn size determine treatment?
Burn size is one factor. Depth, cause, body area involved, and complications also influence care decisions.
Educational note
This resource supports first aid awareness and workplace safety education and does not replace assessment by trained emergency or healthcare professionals.
