Eustachian Tube Infections: Symptoms, Treatment & When to Seek Care (Canada)
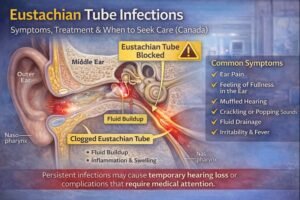
Eustachian tube infections are common in young children under six, largely due to anatomical differences in their ear structures. While many cases resolve with home care and medications, untreated or severe infections can lead to temporary hearing loss or complications.
Common Symptoms
Eustachian tube dysfunction or infection may cause:
-
Ear pain or pressure
-
Temporary hearing changes or muffled hearing
-
Popping or crackling sounds
-
Irritability in young children
-
Fever (in infectious cases)
-
Balance discomfort in some cases
Treatment Options
Pain Management
Medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen may help reduce ear pain and fever. These are available over-the-counter across Canada.
⚠ Do not give aspirin to children under 18, as it has been linked to Reye’s syndrome, a rare condition affecting the liver and brain.
Decongestants & Allergy Relief
Eustachian tube infections often follow colds, sinus congestion, or seasonal allergies. Decongestants or doctor-directed allergy medications may help reduce swelling and improve drainage.
Young children should not receive decongestants without guidance from a healthcare provider.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are only effective for bacterial causes — not viral infections. Broad-spectrum antibiotics may be used if symptoms worsen or fail to improve.
Individuals allergic to penicillin (including amoxicillin) should notify their provider to avoid reactions.
Surgical Considerations
In some cases, enlarged adenoids can block drainage and contribute to recurring infections. An ENT specialist may recommend removal in persistent or complex cases.
When to Seek Medical Care
A doctor should assess:
-
Ear pain lasting more than 48–72 hours
-
Fever that persists or rises
-
Hearing changes or balance issues
-
Recurrent infections
-
Symptoms in very young children
First Aid & Canadian Training Context
While Eustachian tube infections are managed by medical professionals, related ear pain, fever, and irritability are common concerns in child care settings, workplaces, and recreational programs.
Through St. Mark James Training (stmarkjamestraining.ca), Canadians learn to recognize health-related symptoms that may require monitoring, documentation, or escalation to medical care — valuable in:
-
Childcare & day camps
-
Coaching & sport programs
-
Workplace first aid settings
Understanding symptoms early can support safer decision-making until the individual receives medical assessment.
Disclaimer (Non-Diagnostic)
This content is for general information only and is not a substitute for professional medical assessment or treatment. If an infection or hearing change is suspected, consult a qualified healthcare provider in your province or territory.
