Cream Cheese Allergy: Symptoms, Causes, and First Aid Awareness in Canadian Settings
What Is a Cream Cheese Allergy?
Cream cheese is a dairy product made from milk and is considered a major food allergen because it contains milk proteins. Some children—particularly those under age three—develop an allergy to milk and milk-based foods, including cream cheese. Many children outgrow this allergy over time, but a small percentage remain allergic into adolescence or adulthood. Adults can also experience milk-related allergies, sometimes developing symptoms later in life.
Why This Matters for First Aid and Workplaces in Canada
Milk and dairy products are common in Canadian workplaces, schools, childcare centres, and catered events. Cream cheese may appear in bagels, dips, desserts, and prepared foods, sometimes without being obvious. First aid awareness helps people recognize allergic reactions early, respond appropriately, and understand when medical care is required—especially in shared eating environments.
A Realistic Scenario
At a morning meeting, a staff member eats a bagel with cream cheese provided by the office. Within minutes, they notice itching around their mouth and develop mild hives on their neck. A coworker with first aid training recognizes this as a possible allergic reaction, helps the individual avoid further exposure, and follows workplace procedures to monitor symptoms and seek medical assistance when needed.
Common Symptoms of a Cream Cheese Allergy
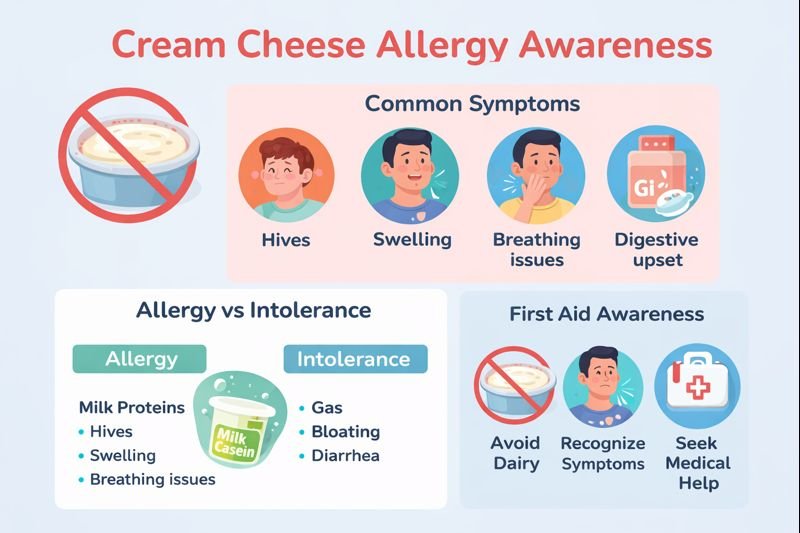
-
Skin: Hives, redness, itching, or swelling
-
Respiratory: Nasal congestion, wheezing, coughing, laboured breathing
-
Digestive: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal discomfort
-
Oral and facial swelling: Lips, tongue, or throat
Symptoms often begin within minutes of exposure but can sometimes progress over a short period of time.
What Causes a Cream Cheese Allergy?
Cream cheese contains milk proteins, mainly casein and whey. Casein makes up about 80% of milk protein and remains in cream cheese after processing. During manufacturing, enzymes such as rennet are used to separate whey from casein, leaving casein concentrated in the final product.
An allergic reaction occurs when the immune system mistakenly identifies these milk proteins as harmful. This triggers the release of immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies and histamine, which leads to the physical symptoms of an allergic reaction.
Some individuals—particularly older children and adults—may show greater sensitivity to casein specifically.
Severe Reactions and Anaphylaxis Awareness
In rare cases, cream cheese allergy can lead to anaphylaxis, a severe, whole-body allergic reaction. This may include:
-
Rapid swelling of the face or throat
-
Difficulty breathing or swallowing
-
Severe digestive symptoms
-
Dizziness, confusion, or fainting due to a sudden drop in blood pressure
Anaphylaxis is a medical emergency and requires immediate professional care. First aid training emphasizes early recognition and rapid escalation rather than treatment decisions.
Allergy vs. Intolerance: What’s the Difference?
A cream cheese allergy involves the immune system reacting to milk proteins.
A dairy intolerance, such as lactose intolerance, does not involve the immune system and occurs when the body has difficulty digesting lactose, the natural sugar in milk.
-
Allergy symptoms: hives, swelling, breathing issues
-
Intolerance symptoms: gas, bloating, nausea, diarrhea
Cream cheese is lower in lactose than some dairy products, so intolerance symptoms are usually milder and less common compared to milk.
Prevention and Workplace Considerations
-
Clear identification of dairy ingredients in shared foods
-
Allergy-aware food handling and catering practices
-
Encouraging disclosure of food allergies where appropriate
-
Training staff to recognize allergic reactions and follow response plans
-
Extra caution in childcare, healthcare, and food service environments
Prevention and preparedness are key components of workplace safety education.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is cream cheese a common allergen?
Cream cheese contains milk, which is one of the major food allergens recognized in Canada.
Can children outgrow a cream cheese or milk allergy?
Yes. Many children outgrow milk allergies, although some remain allergic into later childhood or adulthood.
Can adults develop a cream cheese allergy?
Yes. Some adults develop sensitivity to milk proteins, including casein, later in life.
How quickly do symptoms appear after eating cream cheese?
Symptoms often begin within minutes, but timing can vary depending on the individual and sensitivity level.
Why is first aid training important for dairy allergies?
Training helps people recognize symptoms early, stay calm, and activate emergency procedures when needed.
Educational Note
This article is intended for general first aid and workplace safety education in Canada. It supports awareness and preparedness but does not replace individual medical assessment or emergency care.
