Cosmetic and Toiletry Reactions: Irritation, Allergies, and First Aid Awareness in Canada
Understanding Reactions to Cosmetics and Toiletries
Cosmetics and toiletries are widely used to support hygiene, comfort, and personal appearance. Most people use these products safely every day. However, skin reactions—such as irritation or allergies—are fairly common and often underrecognized. These reactions can affect people of all ages and may occur even after long-term use of a product.
Understanding the difference between irritant reactions and allergic reactions is an important part of first aid and workplace health awareness.
Why This Matters for First Aid and Workplaces in Canada
Cosmetics and personal care products are commonly used in Canadian workplaces, schools, healthcare settings, salons, and shared facilities. Skin reactions can affect comfort, concentration, and safety—especially when irritation involves the face, eyes, or hands. First aid awareness helps workers recognize early signs, reduce exposure, and respond appropriately without escalating symptoms.
A Realistic Scenario
An employee starts using a new facial cleanser before work. Within minutes, their skin begins to sting and feel tight, especially around the eyes. A coworker trained in first aid recognizes this as a likely skin reaction, encourages the employee to stop using the product, gently cleanse the area, and avoid further exposure while monitoring symptoms.
Irritant Reactions
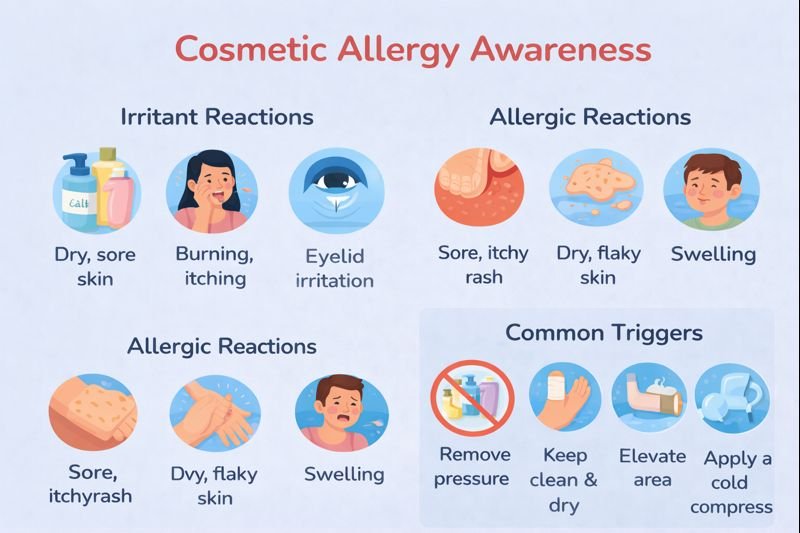
Areas where the skin is naturally thinner or more sensitive are more prone to irritation, including:
-
Face
-
Eyelids
-
Skin folds
Products that may cause irritation include:
-
Shampoos and soaps
-
Liquid foundations
-
Face masks
-
Mascaras
Symptoms of irritant reactions often appear within minutes and may include:
-
Burning or stinging
-
Itching
-
Dryness or soreness
People with sensitive skin or conditions such as dermatitis or rosacea are more likely to experience irritant reactions. These reactions are not allergies and usually improve once the product is stopped.
Allergic Reactions to Cosmetics
Allergic reactions involve the immune system. An allergy usually develops after repeated exposure to a substance, meaning someone can suddenly react to a product they have used for years without problems.
A common form is allergic contact dermatitis, which may cause:
-
Redness and swelling
-
Itchy, sore bumps
-
Dry, flaky, or cracked skin
Reactions are often worse where the product was applied but can spread to other areas. Symptoms typically improve within about a week once exposure stops, although allergies themselves are often long-lasting.
Common Ingredients That Trigger Cosmetic Allergies
Some ingredients are more likely to cause allergic reactions, including:
-
Fragrances (often listed as “parfum”)
-
Fragranced plant extracts such as citrus, tea tree oil, and lavender
-
Preservatives used to prevent bacterial growth
-
Nail products, especially acrylate-based nail enhancements
-
Certain sunscreens
-
Hair dyes, particularly those containing phenylene diamine
Hair dye reactions can be significant and may involve swelling and redness of the scalp, face, ears, and neck—even in people who have coloured their hair for many years without prior issues.
Products labelled “natural” or “hypoallergenic” may still contain common allergens.
First Aid Awareness and Skin Reactions
From a first aid perspective, the focus is on early recognition and reducing exposure:
-
Stop using the suspected product immediately
-
Gently cleanse the affected area
-
Avoid applying additional products to irritated skin
-
Monitor symptoms, especially around the eyes or face
-
Follow workplace procedures if symptoms interfere with work or safety
Severe swelling, widespread reactions, or breathing symptoms require urgent medical attention.
Prevention and Workplace Considerations
-
Use products appropriate for sensitive skin when needed
-
Introduce new products one at a time
-
Be cautious when using shared cosmetics or personal care items
-
Encourage reporting of reactions that affect work duties
-
Maintain first aid awareness for skin and allergic reactions
Education helps reduce repeated exposure and unnecessary discomfort.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between irritation and a cosmetic allergy?
Irritation damages the skin directly, while allergies involve the immune system reacting to a substance.
Can someone become allergic to a product they’ve used for years?
Yes. Allergies can develop after repeated exposure, even without prior reactions.
Are fragranced products a common cause of reactions?
Yes. Fragrances and fragranced plant extracts are frequent triggers.
Do “natural” or “hypoallergenic” products prevent reactions?
Not always. These products can still contain allergens or irritants.
Why is first aid awareness important for skin reactions?
Early recognition and removal of the trigger can prevent worsening symptoms and complications.
Educational Note
This article is intended for general first aid and workplace safety education in Canada. It supports awareness and prevention of skin reactions but does not replace medical evaluation when needed.
